
Source: WANG Dehai, LI Tianjun, GAO Jianen, et al. Construction of quality management system of perinatal stem cell bank [J]. Chinese Journal of Cell and Stem Cells: Electronic edition, 2019,
Tissue repair and regeneration is one of the oldest medical problems. Regenerative medicine refers to the use of biological and engineering theories to promote the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, so that the body can restore normal tissue characteristics and functions. Mesenchymal stem cells (mesenchymalstemcells, MSCs) is one kind has the ability to self-renewal and multi-directional differentiation potential of cells, more is the most widely used in the area of regenerative medicine treatment cell source, healing in tissue repair and regeneration plays a key role.

 Source: CAI Haijun, JIAN Huagang. Research progress on the application of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair and regeneration. Chongqing Medical Science, March 2023, Vol. 52, No. 5
Source: CAI Haijun, JIAN Huagang. Research progress on the application of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair and regeneration. Chongqing Medical Science, March 2023, Vol. 52, No. 5
1. Repair the heart muscle, save the heart
Coronary heart disease and heart failure are the main causes of death of cardiovascular diseases and have become a major challenge in the cardiovascular field in the 21st century. With the aging of the Chinese population, the prevalence of heart failure is increasing rapidly, and the prevalence of people over 70 years old is more than 10%. Traditional drug treatments only delay the symptoms of heart failure, leading to repeated hospitalizations.
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) can realize their migration, differentiation and homing in myocardium through paracrine mechanism, and have immunomodulatory effects, and can survive in the environment of myocardial damage, making them the seed cells of candidate stem cells. hMSCs transplanted into infarcted myocardium can inhibit ventricular remodeling and improve cardiac function. The mechanism of hMSCs is that HMSCS can inhibit myocardial fibrosis and reduce myocardial apoptosis, as well as play a role in immune regulation and promotion of neovascularization.

 来源:张红强, 张冰, 李建奇,等. 间充质干细胞实现心肌修复:机遇与挑战[J]. 医学研究与教育, 2022, 39(5):25-30.
来源:张红强, 张冰, 李建奇,等. 间充质干细胞实现心肌修复:机遇与挑战[J]. 医学研究与教育, 2022, 39(5):25-30.
2. Repair the liver and delay the progression of liver disease
Liver disease is one of the most common diseases in the world. End-stage liver disease is characterized by low cure rate, high cost, rapid metastasis and high mortality. To date, liver transplantation is the gold standard when the liver has suffered irreversible damage. However, organ shortage is still the main limiting factor that liver transplantation cannot be carried out on a large scale.
Mesenchymal stem cells can improve the ability of liver fibrosis and slow the progression of liver disease by inhibiting epithelial mesenchymal transformation and collagen production of hepatocytes, controlling inflammatory response, and inhibiting angiogenesis. Mesenchymal stem cells are expected to be the ideal source of liver stem cell research, especially for the treatment of immune hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver diseases.
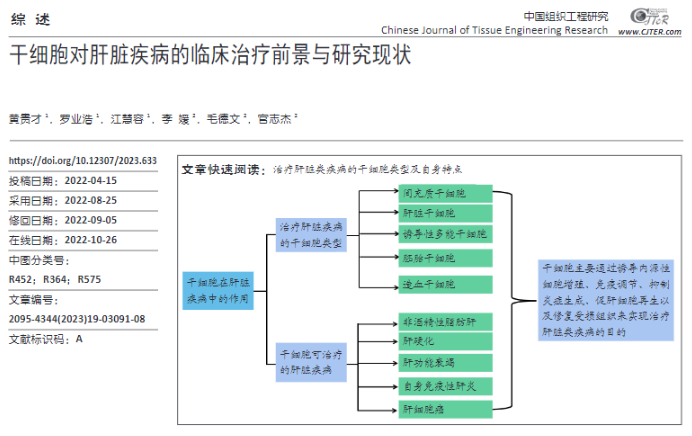
 Source: HUANG Guicai, Luo Yehao, JIANG Huirong, et al. Clinical treatment prospect and research status of stem cells for liver diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering, 2023, 27(19):3091-3098.
Source: HUANG Guicai, Luo Yehao, JIANG Huirong, et al. Clinical treatment prospect and research status of stem cells for liver diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering, 2023, 27(19):3091-3098.
3. Repair intestinal damage and reduce inflammatory bowel disease
The gut is an important part of the human digestive system and the most concentrated part of the microbiome in the human body. Studies have shown that the gut is the central organ of collective stress response, and various stress factors can lead to intestinal structural damage and functional disorders, including local or systemic inflammatory response caused by intestinal barrier function impairment and intestinal structural and functional damage caused by viral factors.
Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells can reduce inflammatory bowel disease and prevent disease recurrence. Clinical trials have confirmed that mesenchymal stem cells can migrate to various sites of inflammation, including areas of intestinal inflammation, colitis and intestinal lymph nodes, etc., and can differentiate into various cells and be transplanted into many tissues to replace inflammatory cells to perform the function of normal cells or secrete soluble factors to stimulate the survival and recovery of injured cells and tissues.

 Source: ZANG Chenghao, Yang Jinwei. Research progress on the effects of mesenchymal stem cells on intestinal flora during intestinal injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Biologics, 2022, 35(9):5.
Source: ZANG Chenghao, Yang Jinwei. Research progress on the effects of mesenchymal stem cells on intestinal flora during intestinal injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Biologics, 2022, 35(9):5.
4. Regenerating specific proteins to speed up ligament repair
Tendon and ligament injuries are common in bone and joint surgery. The strength of the ligament itself is related to the number and size of collagen fibers, and collagen fibers increase with the needs or development of the body during development, but with the increase of age, the formation rate of collagen fibers also slows down. Therefore, once the ligament is damaged, the repair process is usually slow and the whole process is complicated and lengthy.
Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells are a kind of MSCs family with strong differentiation ability. In addition to inherits the biological characteristics of MSCs, human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can significantly up-regulate the expression of ligament-specific genes and improve the synthesis rate of ligament-specific proteins after induction in vitro. Therefore, human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells have become one of the important sources of ligament tissue engineering seed cells. During the induction of hAMSCs in vitro, it was found that the highly related genes were ligament fibroblast related genes and angiogenesis related genes, which could enhance the synthesis of ligament fibroblast related proteins, accelerate the regeneration of microvessels, and accelerate the speed of ligament repair.

 Source: Qian Dikun summary, Wu Shuhong proofread. Application of mesenchymal stem cells in ligament tissue repair [J]. Hainan Medicine, 2022(010):033.
Source: Qian Dikun summary, Wu Shuhong proofread. Application of mesenchymal stem cells in ligament tissue repair [J]. Hainan Medicine, 2022(010):033.
5. Improve reproductive organ function and restore fertility
Stem cells can be differentiated into functional cells of different germ layers. Autologous transplantation can repair damaged tissue and improve tissue and organ function. At present, it has received much attention in the treatment of various system diseases, especially degenerative diseases and organ failure, and is considered as a new hope to solve such diseases. Reproductive system diseases are mainly caused by dysfunction or structural damage, which leads to weakened reproductive ability. Stem cells from different sources can improve the function of reproductive organs and restore fertility through various mechanisms, which has become a research hotspot at present.

Source: LIU Zijun, Chang Hui, WANG Yu, WU Xiaoke Research progress of stem cell therapy for reproductive system diseases [J]. Journal of Reproductive Medicine, Volume 30, Issue 6, June 2021
At the moment, Diseases covered by MSCs medicine include autoimmune diseases (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease, type 1 diabetes), graft-versus-host disease, orthopedic diseases (e.g., knee arthritis, degenerative disc disease), cardiomyopathy, lung diseases (e.g., acute respiratory distress syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), acute and chronic wound repair (e.g., burns, diabetic foot), neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., diabetes foot), and neurodegenerative diseases. Such as Parkinson's disease), the clinical research of MSCs is developing rapidly.

Source: CAI Haijun, JIAN Huagang. Research progress on the application of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair and regeneration. Chongqing Medical Science, March 2023, Vol. 52, No. 5
Stem cells are classified into embryonic stem cells, perinatal stem cells and adult stem cells according to their developmental stages. Perinatal stem cells refer to stem cells in the umbilical cord and placenta tissue, which are necessary for the development and growth of the fetus in the mother. It has been found that perinatal stem cells not only have higher proliferation and differentiation ability than adult stem cells, but also perinatal tissues become a good source of stem cells due to their sufficient supply, convenient source, safe clinical use, and minimal ethical and legal disputes.
