
Source:eMedClub News
MiNA Therapeutics, a pioneer in small activated RNA (RNAa, saRNA), has published data from the latest preclinical in vivo study of its RNAa product for fetal hemoglobin (HbF), demonstrating for the first time that RNAa therapy can be efficiently delivered to red blood cell progenitors in the bone marrow to effectively treat beta-hemoglobinopathy. The field of hematopoietic stem cells is about to usher in new branches and competitions of gene therapy.
MiNA's HbF products are designed to increase transcription of the gamma-globin (HBG) gene, enabling beta-hemoglobin patients to produce higher levels of HbF as a compensatory form of hemoglobin, with the potential to achieve a functional cure for patients with severe inherited blood disorders such as sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
In non-human primates, MiNA encapsulates the RNAa complex in liposome NOV340, which can be delivered intravenously to the bone marrow, achieving more than 60% of erythrocyte colony-forming unit (CFU-E) cells and preerythroblasts (Pro-E). The same level of delivery efficiency was observed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Current situation and development trend of hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy
With the world's first CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing therapy Casgevy successively approved by the US FDA for two indications, hematopoietic stem cell gene editing therapy has also attracted more attention.
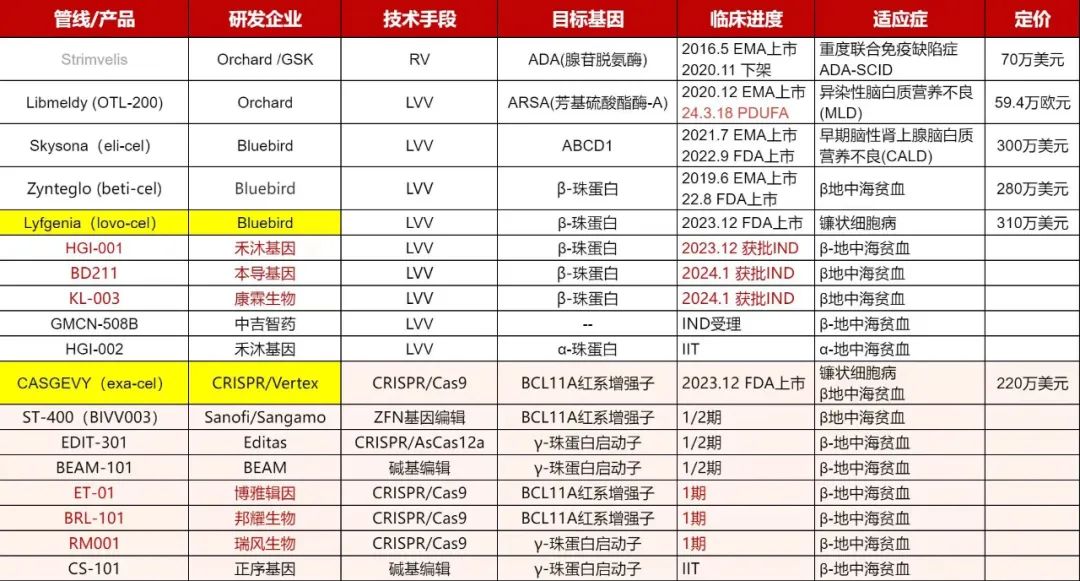
As early as 2016, the world's first hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy Strimvelis was listed in Europe, and in the following years, Blue Bird biological Zynteglo, Skysona, Orchard's Libmeldy have been listed, and the most approved indication is thalanaemia. At present, the conventional clinical treatment of thalassemia is regular blood transfusion or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, although effective, but the side effects and accompanying long-term treatment needs also caused great distress to patients, and gene therapy can better avoid these shortcomings, is expected to become the main treatment of the disease in the future, the market prospect is huge.
In the face of the mature technology of existing products on the market in terms of CMC process and production cost, gradually overcome the commercialization problems; Gene-editing tools continue to iterate and optimize, deepening their advantages in precision, simplicity and efficiency, and RNAa therapies that have just won their ticket seem to be a bit behind the pace. However, RNAa does not change the genome, using the inherent gene activation mechanism to restore or promote the normal function of genes on a small scale, and thus the mechanism of protein regulation pathway in the cell, but also in the master of the gene therapy track unique. After licensing the basic patent for saRNA in 2014, MiNA began clinical studies of the world's first saRNA drug, McL-cebpa, in 2016, with outstanding results for advanced liver cancer. The announcement of the results of the MiNA preclinical study undoubtedly indicates that the field of hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy is about to usher in the impact of new therapies, opening a new round of technical optimization and competition.