
Source:International stem cell research
Stem cell research is a dynamic and rapidly developing field with many important research advances in recent years. Stem cells have important roles and functions in repairing the immune system, respiratory system, digestive system, blood circulation system, endocrine system and nervous system.
01 Immune System
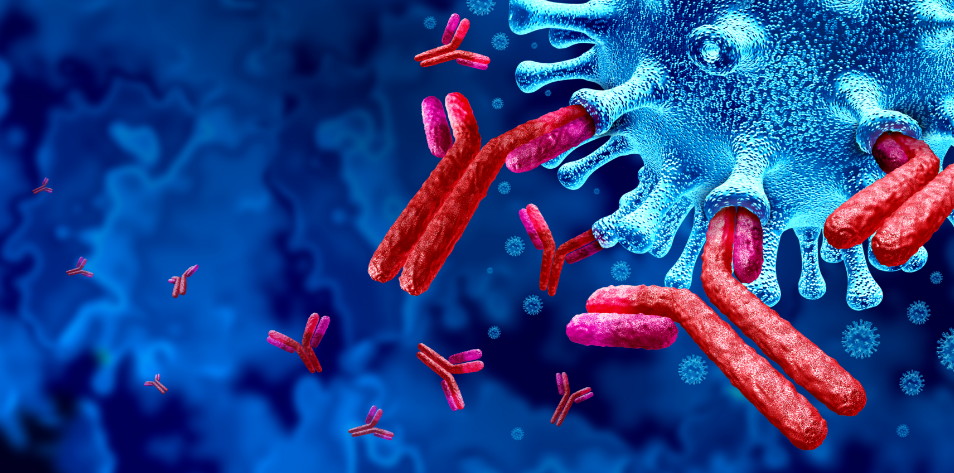
Stem cells play a key role in immune system repair. They have the ability of self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, and can differentiate into a variety of immune cells, such as T cells, B cells and macrophages, so as to enhance the number and function of immune cells. Stem cells can help repair damaged immune tissue, enhance the body's immune response, and promote balance in the immune system.
02 Respiratory System
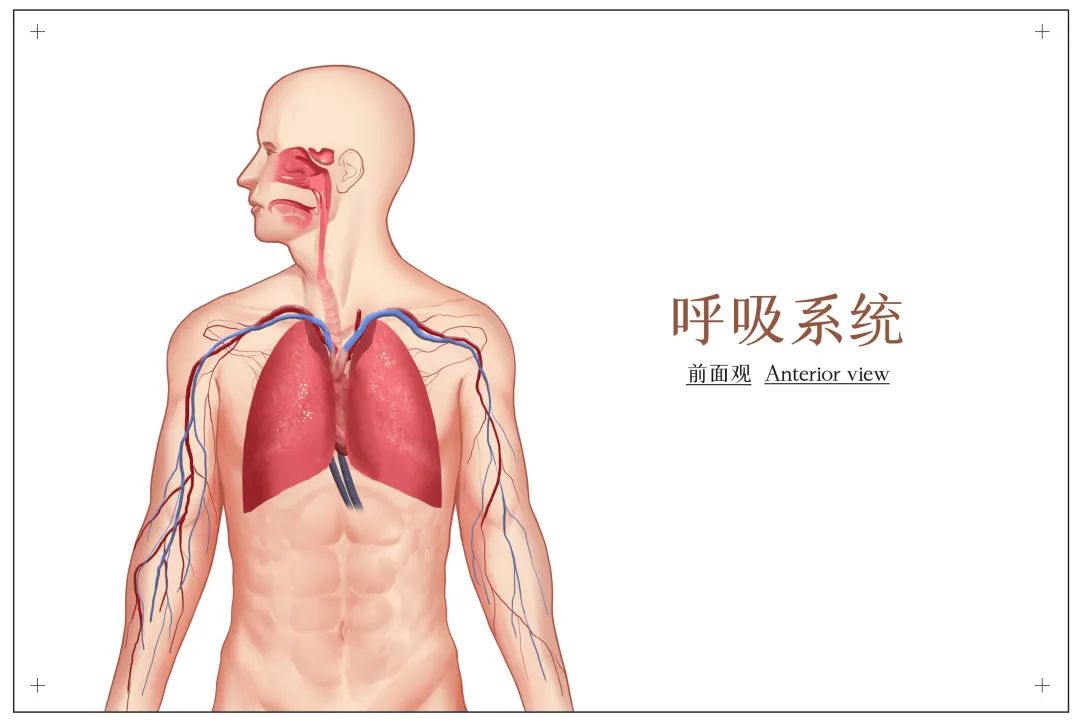
Stem cells have potential in respiratory system repair. In lung injury and disease, stem cells can differentiate into respiratory cells such as alveolar epithelial cells and bronchial epithelial cells, promoting regeneration and repair of damaged lung tissue. In addition, stem cells can also secrete a variety of growth factors and anti-inflammatory factors, reduce inflammatory response, promote lung tissue repair and regeneration.
03 Digestive System
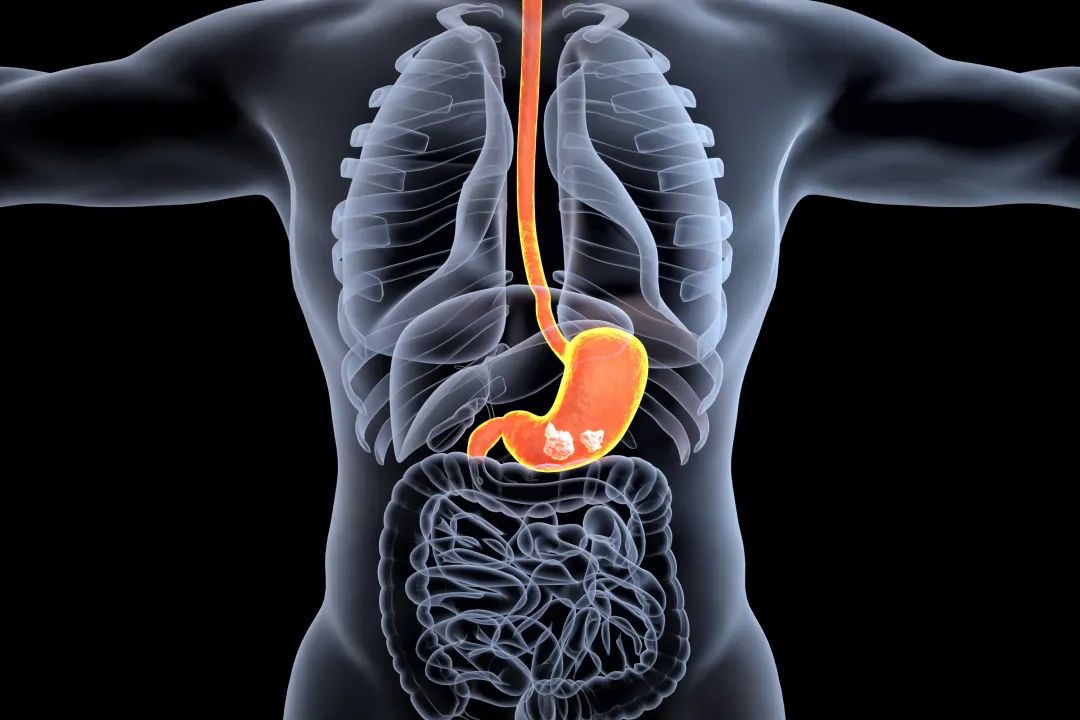
Stem cells play an important role in digestive system repair. For example, stem cells can differentiate into intestinal epithelial cells, promoting the regeneration and repair of intestinal mucosa. In addition, they can secrete a variety of cytokines and growth factors, regulate the balance of the gut microbiome, improve intestinal barrier function, reduce inflammatory response, and promote the repair of the digestive system.
04 Blood circulation system
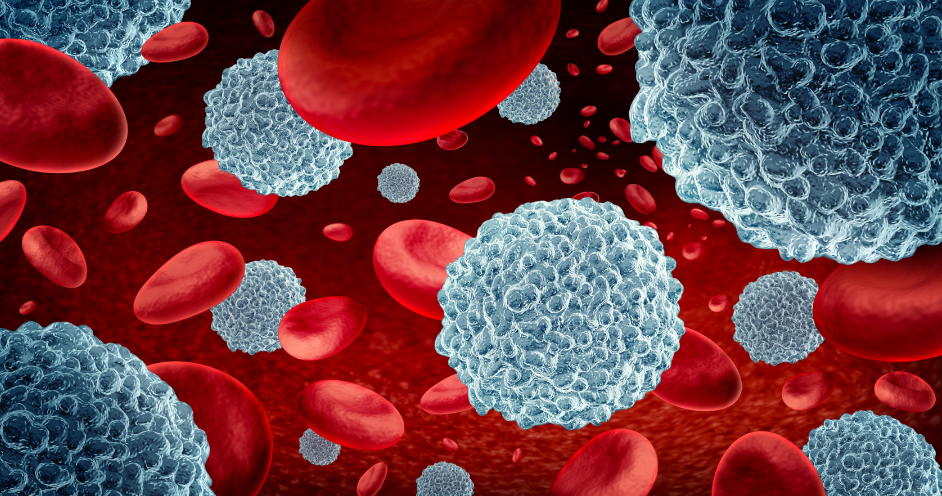
Stem cells play a significant role in the repair of the blood circulation system. Hematopoietic stem cells are a special kind of stem cells, which have the ability of self-renewal and multi-differentiation, and can differentiate into all kinds of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. By transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells, some diseases of the blood system can be treated, such as leukemia, aplastic anemia, and so on, to promote the regeneration and repair of blood cells.
05 Endocrine System
Stem cells also play an important role in the repair of the endocrine system. For example, in insulin-dependent diabetes, the function of islet cells is impaired, resulting in reduced or complete loss of insulin secretion. Stem cells can differentiate into islet beta cells, replace damaged islet cells, restore insulin secretion function, and thus improve blood sugar control. In addition, stem cells can also secrete a variety of growth factors and hormones, regulate the balance of the endocrine system, and promote tissue repair and regeneration.
06 Nervous System
Stem cells show great potential in the repair of the nervous system. Neural stem cells are a kind of stem cells with self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation ability, which can differentiate into a variety of nerve cells, such as neurons and glial cells. Transplantation of neural stem cells can promote the regeneration and repair of damaged nerve tissue and improve nerve function. In addition, stem cells can also secrete a variety of neurotrophic factors and growth factors, provide support and protection of nerve cells, and promote the repair and regeneration of the nervous system.
In general, stem cells play an important role and function in the repair of the immune system, respiratory system, digestive system, blood circulatory system, endocrine system and nervous system. With the continuous progress of science and technology, stem cell therapy is expected to provide a new direction and hope for the treatment of related diseases. However, when applying stem cell therapy, more research and clinical practice are needed to ensure its safety and efficacy.