
According to the latest research and clinical data, intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe with no serious side effects or adverse reactions. The researchers conducted an extensive scientific literature search on serious adverse events related to intravenous injection of mesenchymal stem cells. It covers multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ankylosing spondylitis, weakness, autism, cerebral palsy, diabetes, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, lupus, Parkinson's disease, scleroderma, spinal cord injury and traumatic brain injury. The results showed that correct intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells was very safe, and there were few reports of serious adverse events related to their use. Today, we review the literature and summarize the evidence for the safety of intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been proved to reduce inflammation and promote healing because of their immunomodulatory characteristics and the secretion of growth factors, so they have been used in the treatment of many diseases. Intravenous infusion is the most common way to transport mesenchymal stem cells, including arterial infusion, intrathecal injection, intranasal administration and so on. As a new method of cell therapy, intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been the focus of research and application. According to the latest research and clinical data, intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe with no serious side effects or adverse reactions.
Today, by summarizing the literature in recent years, we take stock of the evidence for the safety of intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells.
Evidence 1: thousands of cases show that intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe
Researchers from the American Foundation for Regenerative Medicine published a review in the journal Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy and conducted an extensive scientific literature search on serious adverse events related to intravenous injection of mesenchymal stem cells. It covers multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ankylosing spondylitis, weakness, autism, cerebral palsy, diabetes, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, lupus, Parkinson's disease, scleroderma, spinal cord injury and traumatic brain injury.

The authors verified that in thousands of intravenous injection cases, only two severe adverse reactions (SAE) occurred, resulting from two upper limb thromboembolism patients with previous kidney disease, and these two patients did not leave any sequelae and had no pulmonary embolism. In the end, the authors concluded that correct intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is very safe, and there are few reports of serious adverse events related to their use.
Evidence 2: 15-year clinical data confirm that intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe

In a meta-analysis in the journal Stem Cell Research&Therapy, the authors reviewed clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cells over the past 15 years, identified all treatment-related adverse events associated with the administration of mesenchymal stem cells, and explored the safety of mesenchymal stem cells in clinical application.
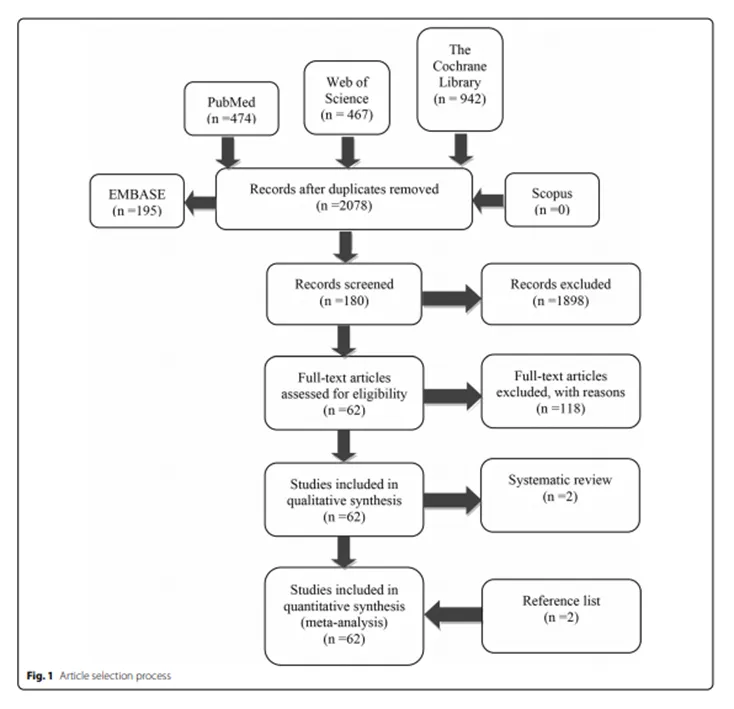 Conclusion: for 15 years, 3546 patients, 62 clinical studies confirmed that mesenchymal stem cells are clinically safe!
Conclusion: for 15 years, 3546 patients, 62 clinical studies confirmed that mesenchymal stem cells are clinically safe!
Evidence 3: randomized trials confirm that intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe.
An article in the Lancet magazine Eclinical Medicine confirmed the safety of mesenchymal stem cells through a review of clinical randomized trials of mesenchymal stem cells conducted between 2012 and 2019.

This study analyzed the possible adverse reactions of mesenchymal stem cells in randomized clinical trials, including acute adverse reactions within 24 hours, infection, thrombosis, and long-term events such as mortality and malignant tumors.
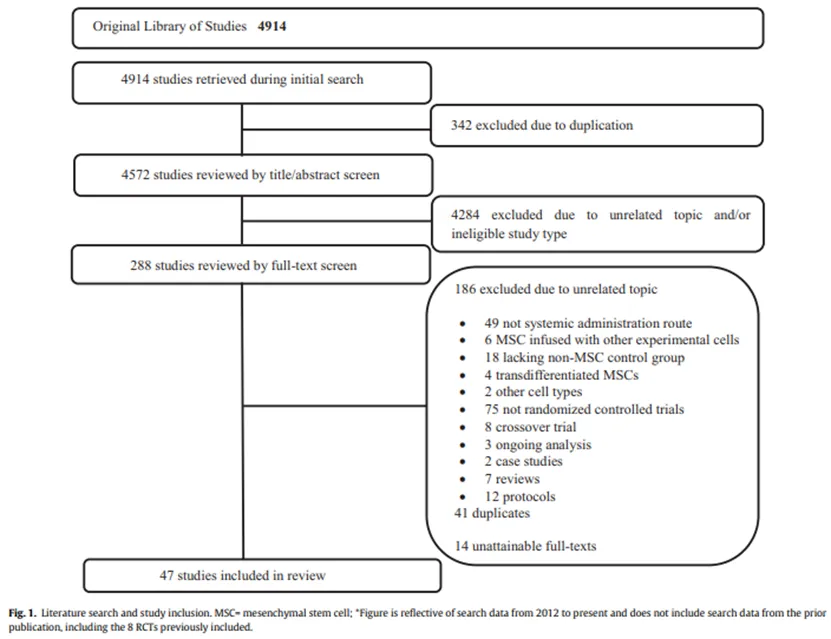
The results showed that there was no relationship between mesenchymal stem cell therapy and the development of acute transfusion toxicity, infection or malignant tumor without fever, and no link was found between mesenchymal stem cell therapy and the development of thrombus.
Evidence 4: intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is safe for a variety of diseases.
As mentioned above, intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is considered to be a relatively safe treatment in clinical practice and has been verified in a variety of diseases. These types of diseases include but are not limited to the following:
Cardiovascular disease: Hare et al verified that intravenous infusion of 1 × 10 ^ 8 allogeneic and autologous mesenchymal stem cells is safe and effective in the treatment of patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, and the incidence of major adverse cardiac events is within a controllable range.
Immune diseases: studies have confirmed that a single intravenous infusion of MSCs is safe and well tolerated, indicating that the treatment is effective, and there are no adverse events related to administration, and all participants can well tolerate intervention treatment.
Liver disease: Wang et al found that intravenous injection of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (0.5 × 10 ^ 6 cells / kg) in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is feasible and well tolerated.
Pulmonary disease: intravenous injection of allogeneic BMSCs cells is considered safe and feasible in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
These research results provide theoretical basis and practical experience for the application of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of more diseases.
Although mesenchymal stem cell therapy is safe in most cases, there are still some precautions. First of all, patients should be fully aware of the risks and possible effects of treatment before receiving treatment. Secondly, mesenchymal stem cell therapy should be carried out under the guidance of professional doctors to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. Medical institutions must strengthen the supervision of stem cell treatment to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. Finally, future research needs to explore in more detail the safety of mesenchymal stem cell therapy under different populations and treatment options, and strengthen the monitoring and reporting of adverse events.
Summary.
So far, more and more data have confirmed the strong potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment or regeneration of various diseases, promoting the treatment of many diseases in clinical work. Intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells is a very common mode of drug administration, and its safety has been effectively verified, which means that this mode of drug administration can be used according to the actual needs in the future. However, the efficacy and safety of treatment may also be affected by individual differences, disease status and treatment options and other factors, so in practical application also need to be carefully evaluated in the light of specific circumstances.