
With the impact of the aging population, bone diseases are widespread in society, including acute and chronic diseases. They can affect any part of the musculoskeletal system, namely bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints and nerves. Its incidence and impact on public health are increasing year by year, and some serious symptoms, such as long-term pain and limited movement, damage the well-being and quality of life of patients with bone diseases.
Skeletal
Bone is an important part of the human body, which is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments and tendons. Bones support our bodies, protect important internal organs such as the brain and heart, and realize the motor function of the body together with joints and muscles. Bone is also the mineral salt reservoir of hematopoietic organs and the body, which has important endocrine functions and participates in the energy metabolism of the body. Maintaining bone health is very important to maintain the health of the life cycle.
Bone disease is typically characterized by pain (usually persistent pain) and limited mobility, dexterity and overall function, and reduced ability to work.
1. Joint problems, such as osteoarthritis (joint degenerative disease), rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune disease with synovitis as the main pathological basis, high disability rate), psoriatic arthritis (chronic progressive inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis mainly involving the spine and / or peripheral joints), gout (crystals deposited in joints and soft tissues caused by disorders of uric acid metabolism.
Causes acute inflammatory arthropathy), ankylosing spondylitis (chronic inflammatory arthropathy, which mainly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, and may lead to spinal curvature and stiffness).
2. Bone problems, such as osteoporosis (metabolic osteopathy, decreased bone mineral density and destruction of bone microstructure, resulting in fragile bones and prone to fractures), osteopenia, brittle fractures, traumatic fractures.
3. Muscle problems, such as myasthenia.
4. Spinal problems, such as back and neck pain.
5. Problems in multiple parts or systems of the body, such as musculoskeletal local and widespread pain and inflammatory diseases (connective tissue disease and vasculitis, etc.), such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Bone diseases can be caused by a variety of factors, including heredity, age, sex, weight, malnutrition, lack of exercise, smoking and drinking.
Stem cells effectively treat musculoskeletal diseases.
Current treatments are often limited to symptom management or temporary replacement with inert substances rather than prevention and treatment. Alternative biological methods are urgently needed for the treatment of bone diseases. The rapid emergence of stem cell technology provides a new solution for the treatment of bone diseases. at present, some preclinical and clinical studies have been carried out, and it is possible to use regenerative therapy to help these diseases in an effort to provide more effective treatment options.
1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in the treatment of bone diseases.
MSC exists in almost all tissues and is not recognized by the immune system because it does not express histocompatibility complexes and immunostimulatory molecules. It has low immunogenicity and is a "star" in cell therapy, tissue engineering and other related fields. At present, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC), adipose mesenchymal stem cells (ASC) and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSC) have been studied deeply.
1) Bone regeneration.
MSC has good osteoblast differentiation ability. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) can promote MSC to differentiate into osteoblasts. Because of its strong paracrine function, BMP-2 can secrete a large number of factors such as insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β 1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and so on, which effectively promote angiogenesis and bone regeneration.
In recent years, it has been found that BMSC combined with organic materials (such as bovine cancellous bone, collagen sponge, polylactic acid and allogeneic bone transplantation) and inorganic materials (such as hydroxyapatite) can significantly promote the healing of critical cranio-maxillofacial bone defects in mice, play an important role in critical femoral defects in rats and rabbits, and induce spinal fusion in rabbits. It has been proved that local implantation of BMSC can promote the fusion of human lateral spine and repair long bone defects. ASC can also be used to repair critical skull defects in animal models, and it can also be used in combination with a variety of scaffolds (such as type I collagen matrix, coral scaffold, collagen-ceramic composite scaffold, etc.) to guide bone repair. In summary, MSC shows great potential in the field of regenerative medicine such as fracture and bone regeneration, and provides a new strategy for clinical treatment of bone defects.
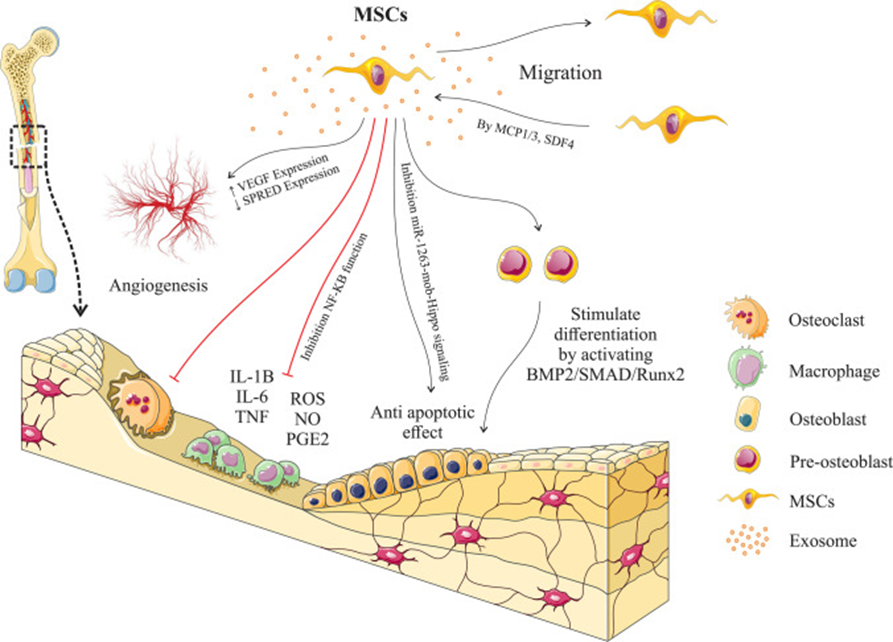
MSC can promote bone regeneration.
2) Cartilage repair.
The self-repair ability of the body after cartilage injury is limited, and the repair of cartilage defects is one of the major challenges faced by plastic surgeons. Implantation of engineered cartilage can improve the success rate of surgery and accelerate the repair of injury. the chondrogenic characteristics of MSC can provide sufficient cell source for engineered cartilage and provide a new direction for repairing cartilage injury.
In 1994, MSC was first applied to the repair of human cartilage. The researchers inoculated MSC into collagen gel to treat the full-thickness defect of cartilage in rabbit femur. Compared with the control group, MSC mixed collagen treatment group is more beneficial to the recovery of rabbit cartilage tissue.In recent years, more and more animal experiments and clinical trials have shown that new bioactive three-dimensional scaffolds (hydrogel and fiber scaffolds) combined with MSC can show excellent therapeutic effect in cartilage injury.
3) Regeneration of other connective tissue.
MSC can mediate the regeneration of other connective tissues, including meniscus, tendons and ligaments, and intervertebral discs. Although current studies believe that MSC can not repair tendon injury, it can only delay the progression of the disease, but the positive role of MSC in meniscus regeneration has attracted more and more attention. In addition, the clinical trial results of MSC transplantation in the treatment of lumbar disc degeneration also show that MSC transplantation has a better prognosis than conventional treatment. Other clinical studies have shown that percutaneous injection of autologous bone marrow concentrated cells can relieve long-term lumbar discogenic pain in patients with degenerative intervertebral disc. It can be seen that MSC transplantation also plays an important role in promoting connective tissue regeneration.
2. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) in the treatment of bone diseases.
The application of iPSC technology in the treatment of bone diseases is still in the stage of research and development, and there is no extensive clinical application at present. IPSC technology is mainly by reprogramming adult cells into pluripotent stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteocytes and chondrocytes, so they can be used to treat bone diseases in theory.
Although iPSC technology has a broad application prospect in the treatment of bone diseases, there are still some challenges, including how to ensure the safety and effectiveness of iPSC differentiated cells and how to produce cell products with stable quality on a large scale. In addition, the problem of immune matching is also one of the key problems to be solved in iPSC treatment.
Generally speaking, iPSC technology provides new ideas and possibilities for the treatment of bone diseases, but in order to achieve clinical application, more research is needed to overcome technical and application obstacles. With the continuous development and maturity of iPSC technology, it is expected to make a breakthrough in the treatment of bone diseases in the future.
3. Stem cell drugs for the treatment of bone diseases.
At present, the stem cell products approved worldwide are mainly concentrated in Japan, South Korea, the United States, the European Union and other places. Here is some information about some stem cell drugs that have been put on the market to treat bone diseases:
1) Chondrocelect:In October 2009, the European Drug Administration (EMA) approved the marketing of somatic cell therapy products from TiGenix of Belgium to repair cartilage injuries to the knee. The product is an autologous chondrocyte implantation called chondrocyte implantation (CCI--, a surgical procedure for cartilage defects) and combines debridement (preparation of defective beds), physical sealing (placement of biofilms, preferably collagen membranes) and rehabilitation.
2) Cartistem:In January 2012, the Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) approved stem cell products for the treatment of degenerative arthritis and knee cartilage injuries. The Chinese name is Kotli, developed by the Korean company Medipost, and the main component is UC-MSC.
3) Maci:In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Maci (autologous chondrocytes cultured on porcine collagen membrane) for clinical treatment of adult knee cartilage injuries. The product is the first FDA-approved product to use tissue engineering to grow cells on scaffolds, using healthy cartilage from the patient's own knee.
4) StemOne:This is an allogeneic cell therapy for knee arthritis approved by the General Administration of Drug Control of India, developed by Stempeutics, which can avoid or delay total knee arthroplasty in patients with acute knee osteoarthritis.
At present, Chinese mainland & Johnson has no stem cell product on the market, but a number of clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cell drugs have been implicitly approved by the Drug Evaluation Center of the State Drug Administration (CDE), involving osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases. With the increase in the number of clinical trials, it is expected that more stem cell therapy products will be approved to market in the future.
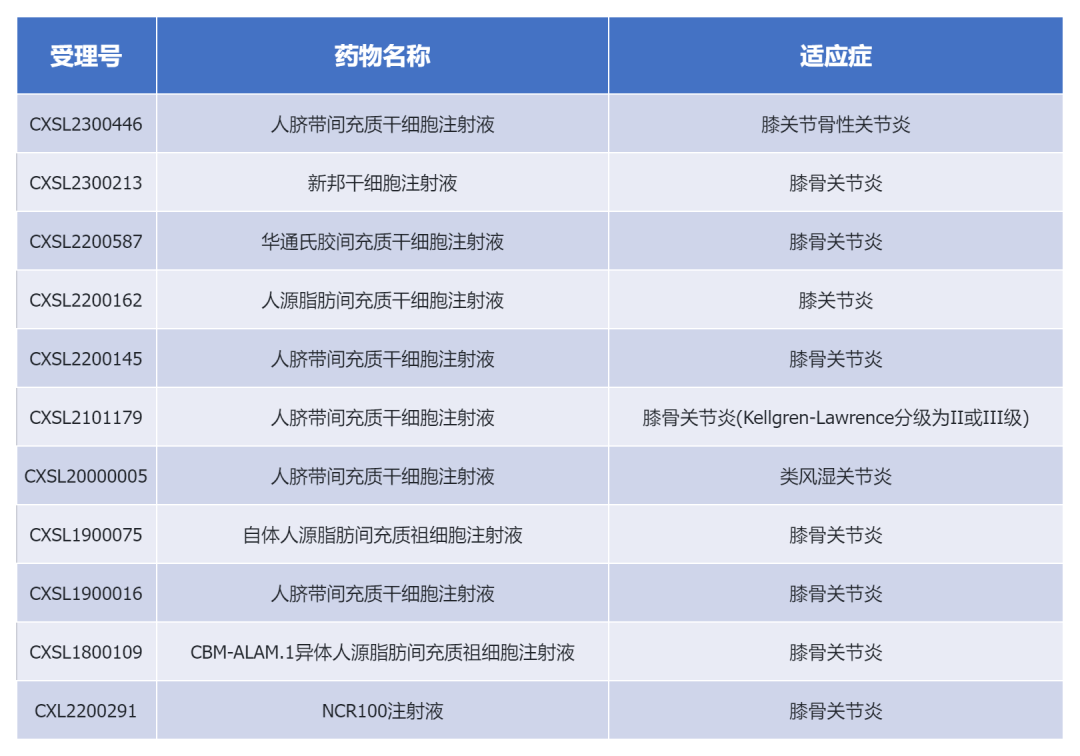
Eleven new stem cell drugs for knee osteoarthritis in China have been approved by IND
Summary.
Stem cell therapy shows the potential to promote tissue repair and relieve pain through the mechanisms of differentiation into chondrocytes, paracrine, anti-inflammation and immune regulation. With the progress of technology and the deepening of research, stem cell therapy will provide revolutionary solutions for the treatment of various bone diseases.
In addition, policy support and capital investment will further promote the research and development and clinical application of stem cell technology, making universal and accurate stem cell treatment possible. It is believed that it will bring safer and effective treatment options for patients and improve their quality of life!