
An expert team from Peking Union Medical College Hospital recently carried out a phase 1 clinical study (ANGE-S003) on "Using intranasal transplantation of human neural stem cells to treat Parkinson's disease." This is the world's first clinical study to treat Parkinson's disease by administering human-derived neural stem cells through the nasal mucosa! Bringing new light to the long-standing problem of Parkinson's disease! What is even more gratifying is that scholars from all over the world have been trying to use stem cells as a new therapy to overcome refractory diseases!

Human-derived neural stem cells: bring new hope to Parkinson's disease!
This phase 1 study conducted by Union Medical College Hospital enrolled a total of 18 patients with advanced Parkinson's disease with a course of more than 5 years (Hoehn-Yahr stage is end 3). After 4 intranasal transplants of human neural stem cells, the results showed:
1. Improvement in Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale score: During the third to 12th months of stem cell therapy, data from the Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) showed that the MDS-UPDRS total score improved significantly (p<0.001). Among them, the improvement was most obvious at the sixth month of treatment, with an average reduction of 19.9 points (95% CI, 9.6 - 30.3;p<0.001).
2. No serious adverse reactions: After treatment, there were no serious adverse reactions related to human-derived neural stem cells, and no mass formation was observed on the brain MRI.
To sum up, after intranasal neural stem cell transplantation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, the patient's function was improved, and the efficacy peaked at the sixth month of treatment. The results of the Phase 1 preliminary study show that treating Parkinson's disease with this method is safe and feasible, and is well tolerated. It is expected to become a new hope and choice for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Let us look forward to follow-up results!
Parkinson's disease science
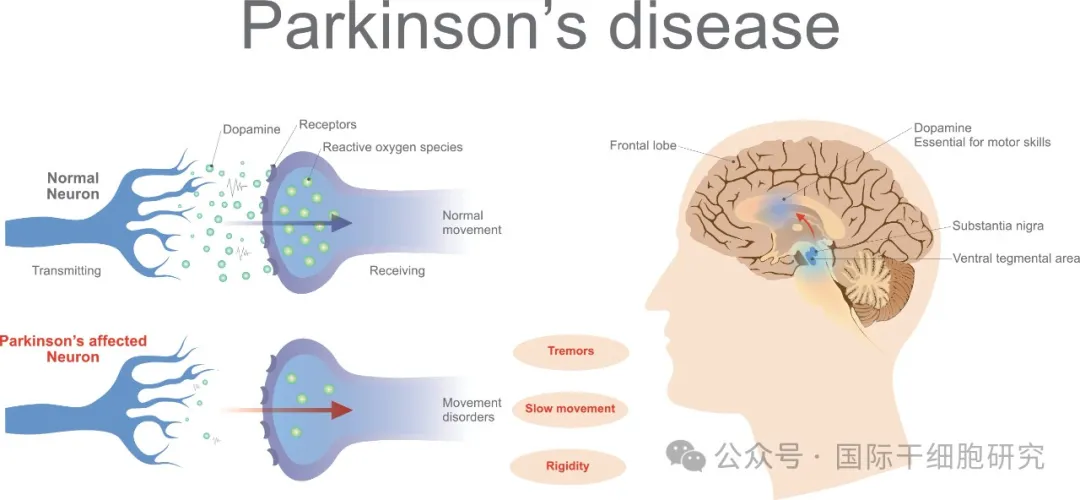
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system. Its typical pathological feature is the progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra. In addition, it is associated with the accumulation of α-synuclein (α-syn) into the Lewy bodies.
The cause of Parkinson's disease is not yet well understood, and may be related to factors such as genetics, aging, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and long-term exposure to harmful substances (such as heavy metals, pesticides, and infectious sources). The main pathological manifestation is the selective loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra of midbrain. These neurons can oxidize dopamine through monoamine oxidase, resulting in the production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Patients may be in dopaminergic neurons. The state of permanent oxidative stress leads to a decrease in endogenous antioxidant levels, which is also the reason why patients with Parkinson's disease usually have increased oxidative stress.
Main clinical manifestations of Parkinson's disease
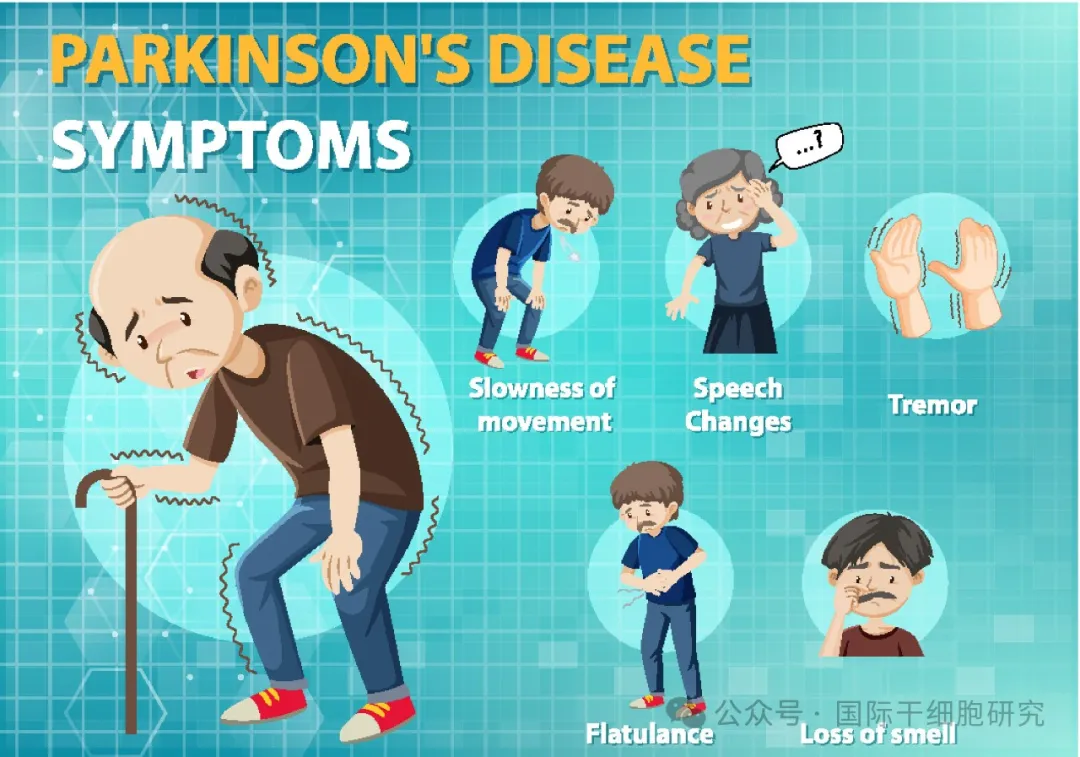
Performance of movement disorders
Patients with Parkinson's disease can experience a series of movement disorders such as static tremor, postural instability, myotonia, and bradykinesia due to insufficient dopamine storage.
non-motor symptoms
1. Sensory disorders: Patients may experience symptoms related to sensory disorders such as limb pain and limb numbness.
2. Autonomic nerve dysfunction: Patients may experience autonomic nerve dysfunction such as hyperhidrosis, orthostatic hypotension, and abnormal urination.
3. Sleep disorders: Patients may see sleep disorders such as multiple dreams at night, shouting, and body dancing.
4. Mental disorders: Some patients with Parkinson's disease may also suffer from mental disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Performance of movement disorders
Patients with Parkinson's disease can experience a series of movement disorders such as static tremor, postural instability, myotonia, and bradykinesia due to insufficient dopamine storage.
non-motor symptoms
1. Sensory disorders: Patients may experience symptoms related to sensory disorders such as limb pain and limb numbness.
2. Autonomic nerve dysfunction: Patients may experience autonomic nerve dysfunction such as hyperhidrosis, orthostatic hypotension, and abnormal urination.
3. Sleep disorders: Patients may see sleep disorders such as multiple dreams at night, shouting, and body dancing.
4. Mental disorders: Some patients with Parkinson's disease may also suffer from mental disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Limitations of traditional treatments for Parkinson's disease
Pathological studies have shown that the development of Parkinson's disease is mainly due to the progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain and the abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein, resulting in the death of dopaminergic neurons.
The above-mentioned treatment methods can neither increase the number of DA nerve cells nor reverse neurodegeneration. Therefore, the curative effect is often unsatisfactory and is usually "treating the symptoms but not the root cause." Therefore, in recent years, stem cells that have the functions of repairing defective necrotic tissues and regenerating nerve cells have become a hot research direction for the treatment of Parkinson's disease!
How do stem cells treat Parkinson's disease?
The main pathological change in Parkinson's disease is the loss of dopamine neurons, which are gradually lost during the onset and development of the disease, and this degeneration is largely irreversible.
With the continuous development of regenerative medicine, researchers are trying to replace dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra with stem cells to replenish the number of dopamine neurons lost in the brain, thereby controlling the continued progress of Parkinson's disease at the source of the cause!
The stem cells currently used to treat Parkinson's disease mainly include mesenchymal stem cells, human induced pluripotent stem cells, neural stem cells and other types. Stem cells are usually differentiated and then transplanted to orient them in vitro and differentiate into specific types of mature cells.
Messages
Parkinson's disease has a history of more than 200 years since its discovery. Its symptoms are severe and the course of disease is long. It is by no means just as simple as "trembling". Moreover, the degradation of dopaminergic neurons is largely irreversible. This has undoubtedly opened up the "hell difficulty" for the treatment of the disease. The emergence of regenerative therapy represented by stem cells is expected to stop the progress of the disease from the source of the cause, bringing a ray of light to patients with Parkinson's disease!
This time, the research team of Union Medical College Hospital has innovatively used stem cell nasal mucosal administration to treat PD, which has left a strong mark in the field of treatment of Parkinson's disease! Xiao Bian hopes that with the efforts of scientific researchers from all over the world, Parkinson's disease will eventually be overcome one day!