
Source: Adult Stem Cell Laboratory
In modern society, diabetes is no longer the exclusive of middle-aged and elderly people, and more and more young people have diabetes.
According to the 10th edition of the Diabetes Atlas published by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (as of November 8, 2021), diabetes caused 6.7 million deaths in 2021, which means that one person dies every five seconds due to diabetes. Among the 537 million patients in the world, the total number of diabetic patients in China is about 140 million, ranking first, and about 1 in 10 people are diabetic patients. It is estimated that by 2045, the number of diabetics in China will reach 174 million.
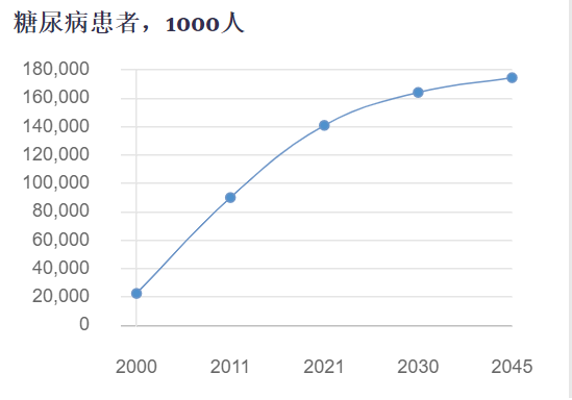 Change curve of the number of diabetic patients in China
Change curve of the number of diabetic patients in China
Why do young people get diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a long-term unhealthy lifestyle, such as stress, obesity, irregular eating and staying up late. In fact, these bad lifestyle habits are the main reason for the young age of type 2 diabetes. Although type 2 diabetes is linked to genetics, environmental factors have a greater influence on the timing of its onset and the progression of the condition.
Diabetes is more difficult to control in younger patients than in middle-aged and older patients. They are often accompanied by a variety of metabolic abnormalities, such as high triglycerides, low high-density lipoprotein, hyperuricemia and microproteinuria. These complications can accelerate the progression of diabetes and lead to more health problems.
How can this challenge be met?
First, we need to recognize that diabetes is not an incurable disease. Lifestyle changes are key to preventing and controlling diabetes. A proper diet, regular rest and rest, adequate exercise and regular medical check-ups are all necessary to maintain good health.
Second, modern medicine offers a variety of treatments for type 2 diabetes, including oral hypoglycemic drugs and insulin injections. The doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan for each patient according to their specific circumstances.
Finally, we should always remind ourselves that youth is not equal to health. But young stem cells may offer new hope for people with type 2 diabetes.
As one of the youngest stem cells, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells have proven to be a promising clinical strategy for the treatment of diabetes.
Latest stem cell research

Professor Mu Yiming et al. from the PLA General Hospital evaluated the efficacy of umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, which was recently published in Stem Cell Translational Medicine.
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is an important indicator for evaluating blood sugar control in patients with diabetes. However, with the development of technology, new indicators such as TIR (Time in Range, time within the target range of glucose) have gradually gained attention in recent years. Because it provides a comprehensive view of blood sugar control, is associated with the risk of diabetes complications, and can improve patients' quality of life. With the advancement of continuous glucose monitoring technology, TIR is easier to measure, providing doctors and patients with a better basis for treatment decisions.
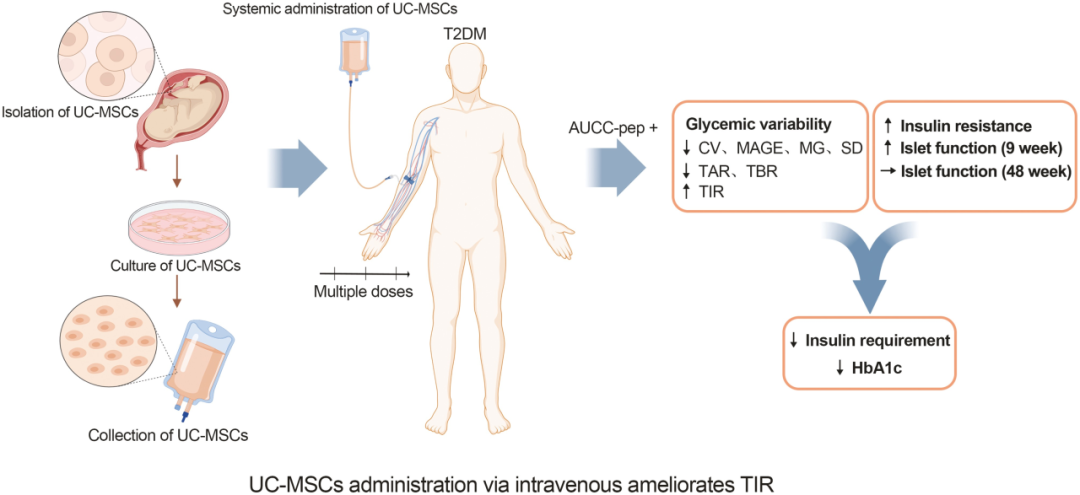
To further evaluate the effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on TIR (Time in Range, time within the glucose target range), the PLA General Hospital team conducted a Phase II clinical study to investigate and evaluate, through retrospective continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults. Efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion.
In this randomized placebo-controlled trial, a total of 73 patients were assigned to receive intravenous infusions of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (n=37) or placebo (n=36) every four weeks for a total of three infusions and were followed for 48 weeks. Changes in TIR and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were assessed at primary endpoints.
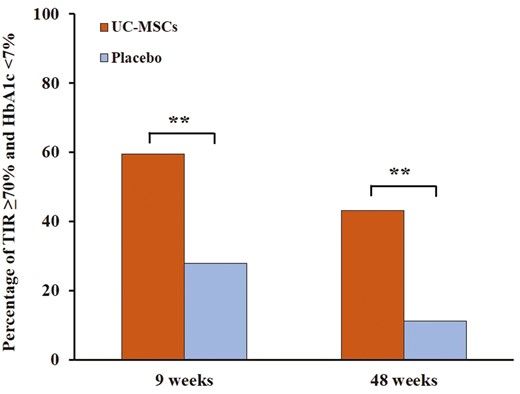
After 48 weeks of treatment, there were significant improvements in TIR and HbA1c in both the umbilical cord and placebo groups compared to baseline. Changes in TIR and HbA1c were more significant in the umbilical cord group compared to the placebo group at 9 and 48 weeks after baseline. More patients in the umbilical cord group met the blood glucose control goals of TIR≥70% and HbA1c<7% at weeks 9 and 48.
To better understand the impact of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes, the researchers further explored the contributing factors. The data showed that stem cells transfused via intravenous infusion significantly increased TIR, while male patients were more likely to benefit from stem cell therapy if they had a higher OGTT test area under the C-peptide curve (AUCC-Pep).
Conclusion
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion may be a potential treatment for adults with type 2 diabetes in China. This study gives us a new perspective on the great potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of diabetes. Of course, more research is still needed to better understand the long-term effects and potential risks of this treatment.