
Source: Chinese Journal of Food and Drug Administration.
The Drug Review Center of the State Drug Administration (CDE) issued the latest article on "China Food and Drug Administration" to explore the scope and classification of China's advanced therapeutic drugs: cellular products are expected to be included in the ranks of advanced therapeutic drugs!
Advanced therapeutic drugs (advanced therapy medicinal product,ATMP), represented by cell and gene therapy products, have brought new opportunities and choices for the treatment of difficult diseases such as cancer, genetic diseases, rare diseases and so on. The field of advanced treatment of clinical high-value traction is developing rapidly, occupying the innovation highland of the global biomedical industry. The global advanced treatment industry is heating up rapidly, and the heat of investment and financing in the industry is high. According to statistics, it is estimated that by 2025, the global gene therapy market will reach 30.54 billion US dollars, and China's market will reach 17.89 billion US dollars.
According to Citeline database statistics, as of April 2024, more than 100 kinds of gene, cell and RNA products have been approved to be put on the market, and more than 3700 products (including about 55% of gene therapy products and 53% of cell therapy products) are in the preclinical or clinical development stage. Although China's advanced treatment industry started relatively late, it has developed into the hottest area of cell therapy research and development in the world. According to the incomplete statistics of ClinicalTrials.gov website, the number of clinical trials and declared products of cell therapy in China ranks second in the world, second only to the United States.
Since the first chimeric antigen receptor T cell (chimeric antigen receptor T cell,CAR-T) therapeutic drug was approved and put on the market in China in 2021, the number of CAR-T products on the market in China has accounted for more than 50% of similar products in the world. The development of China's advanced treatment industry has entered a new stage of "keeping pace with the international advanced level".
Many countries and regions around the world are constantly committed to strengthening the top-level design and regulatory capacity building of the regulatory system of ATMP. American Food and Drug Administration (Food and Drug Administration,FDA), European Drug Administration (European Medicines Agency,EMA), Japanese Pharmaceutical and Medical device Agency (Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Agency,PMDA) and other drug regulatory agencies have gradually established the regulatory framework of ATMP, actively formulated and issued relevant regulations and guidelines, and continuously improved. According to incomplete statistics, regulators around the world have so far issued more than 400 technical guidelines related to cell-related gene therapy products. Some countries and regions have defined the definition and classification of such drugs at the level of laws and regulations, and formulated incentive policies (such as special review procedures, etc.) to speed up product approval and listing.
At present, China's State Drug Administration (National Medical Products Administration,NMPA) has issued more than 30 technical guidelines for such products, covering all stages of research and development, registration, industrial production, and post-market changes. In China, this kind of products are suitable for encouraging innovation, accelerating review and approval and other procedures, but at present, the classification and definition of this kind of drugs have not been clearly defined at the level of laws and regulations, and their names and classification have not yet formed an industry consensus. The disunity of name use and classification is not conducive to standardized supervision, industry communication and international coordination.
The author believes that classification is closely related to industrial development, and it is urgent to clarify the classification and definition of ATMP in China.
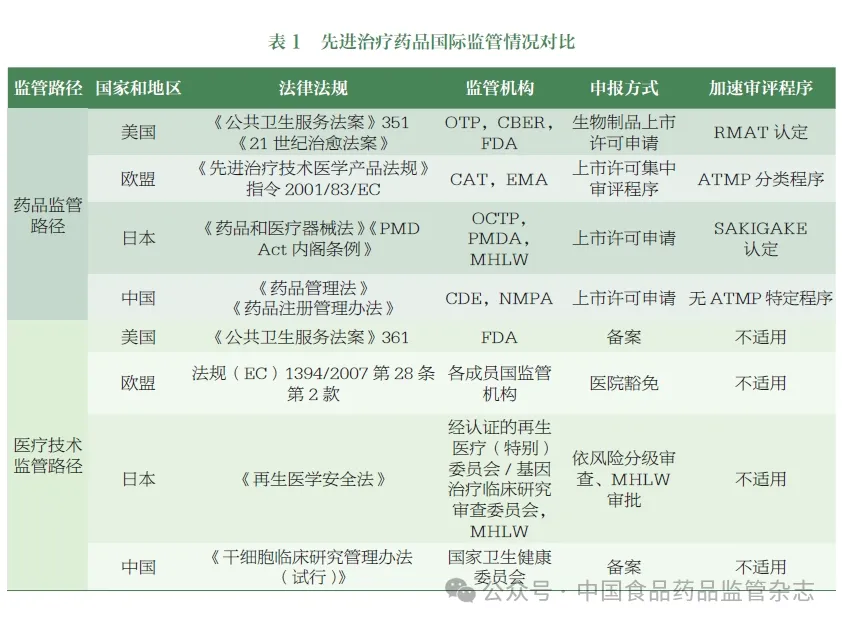
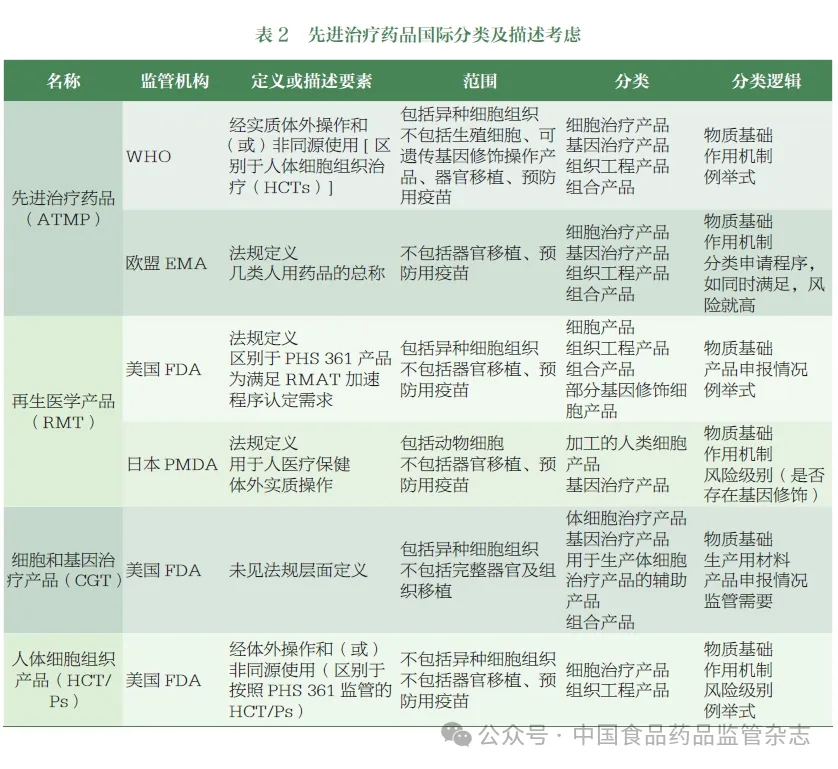
Combined with the investigation of foreign regulatory agencies' ATMP regulatory classification, CDE organized relevant departments to sort out the declaration of relevant domestic products, initially put forward the classification and description of China's ATMP, and held expert seminars. Experts from academia, industry and regulatory fields were invited to discuss the key points to consider the formulation, classification and description of names, and formed the following suggestions.
Suggestions on the Classification and description of ATMP in China
(一) Name and description.
With reference to the names of regulatory bodies such as FDA, EMA, PMDA and WHO, and combined with the terms used in the domestic industry at the present stage, the names of such products should mainly be in line with international standards, while reflecting the innovation and technological advancement of the products, so as to encourage the development of relevant domestic industries, and prospectively reserve regulatory space for future emerging technology drugs. We can refer to WHO and EMA to consider the combination of the general name and the specific classification. Ensure that the general name highlights the attributes of drugs, covers the vast majority of related drug types, and classifies them in detail. Considering that "cell and gene therapy products" mainly reflect the material basis of products, "regenerative medicine products" mainly reflect product functions, and relatively limited, "advanced therapeutic drugs" cover a relatively wide range, and are coordinated with WHO and other international regulatory agencies, it is suggested that "advanced therapeutic drugs" should be used as the Chinese name of such products, and the English name is "ATMP".
WHO issued a technical document in 2023, making it clear that ATMP refers to any cell, gene therapy product or tissue engineering product that has undergone complex in vitro operations and / or non-homologous use. ATMP is usually prepared from somatic cells or tissues by genetic modification and / or in vitro. The types of products include nucleic acid, viral and non-viral vectors, recombinant bacterial cells and recombinant oncolytic viruses. Xenogeneic cells or tissues belong to the category of ATMP, but their complexity is not discussed in the document. The document clearly divides ATMP into cell therapy products, gene therapy products, tissue engineering products and combination products, and defines various products in the noun interpretation section.
Cell therapy product: a cellular product consisting of human nucleated cells, used for cell replacement and tissue reconstruction in the body, and / or for the treatment or prevention of human diseases by regulating the pharmacological, immune, and metabolic state of the cell.
Gene therapy products: drugs containing nucleic acids (plasmids, mRNA, or DNA) that achieve the desired therapeutic effect by regulating, repairing, replacing, adding or deleting specific gene sequences, including non-viral vectors, viral vectors and genetically modified cells, as well as non-recombinant oncolytic virus products.
Tissue engineering products: drugs consisting of human nucleated cells after complex in vitro operations and / or non-homologous use for tissue repair, replacement, reconstruction, or regeneration.
Combination products: ATMP consists of medical devices, stents, matrix and other parts to form a whole drug administration, in which the device or supporting structure helps the overall product to play a therapeutic role.
With reference to the interpretation of this kind of products by international regulatory agencies, and combined with expert opinions, the author thinks that the material basis, technological characteristics, functional uses and so on should be considered in the description of "advanced therapeutic drugs". At the same time, the classification of boundary products related to medical technology is defined based on the degree of in vitro operation and use. Considering that this kind of products are regulated in accordance with drug regulation, the author takes "in vitro operation" and "functional use" as the description elements of ATMP, and according to the current situation and future development trend of related products in China, based on the diversity and innovation of active components to improve the relevant description. It is described as: "Advanced therapeutic drugs refer to cell therapy drugs, gene therapy drugs or tissue engineering drugs produced in vitro and acting in vivo, as well as innovative drugs produced by other advanced technologies / methods." The production and research process of ATMP should meet the ethical requirements of our country. Blood components for transfusion and hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation do not belong to the category of ATMP.
In terms of material basis, we can consider including the current domestic product types with a large number of reports, such as cell therapy products and gene therapy products, as well as tissue engineering products and other emerging technology products, so as to reserve interfaces for new technologies. In terms of process characteristics, combined with the relevant definitions of FDA, EMA, WHO and so on, the cell tissue therapy products prepared by simple operation in vitro and homologous use do not belong to ATMP. Therefore, with reference to the international regulatory practice and combined with the common technological steps of product production, the author defines a simple definition of "in vitro operation" in the description, including separation, purification, amplification, gene modification, gene editing and so on. In the future, if necessary, the definitions of "in vitro operation" and "homologous use" will be further clarified with reference to the practices of FDA and other regulators. In terms of functional use, with reference to the current regulatory situation of domestic biological products, considering that the declared products are mainly therapeutic biological products, so the description is only clearly defined as therapeutic drugs, not related to prevention and diagnosis for the time being.
Combined with the advice of experts, the author further classifies and defines boundary products such as medical technology and products involving the use of germ cells. For medical technologies, it is considered in the description to explicitly exclude medical technologies such as blood transfusion and organ / tissue transplantation that are administered by the National Health Council. It should be noted that the transplant here refers to the treatment of medical institutions, not the way of drug administration. For example, genetically modified hematopoietic stem cells transplanted with drugs also belong to the category of ATMP because of their complex production operations in vitro. For products involving the use of germ cells and some heritable genetic modification operations, because there are many different sources and operations, it is clear in the description that the ethical requirements of our country need to be met.
(二) Classification suggestion.
In order to improve the science and effectiveness of regulation and encourage continuous innovation in drug research and development, combined with the international classification, the material basis of products, the level of regulatory risk and the current situation of domestic product R & D declaration, the author carried out a preliminary study on the classification of ATMP, and discussed the rationality of classification and the ownership of related products.
1. Category division.
In terms of R & D declaration, the type and number of ATMP accepted and reviewed by CDE are increasing year by year, and the number of ATMP clinical trials reported in 2023 reached 13% of the total clinical trials of biological products. As of March 2024, NMPA has approved 5 CAR-T cell therapy drugs and 2 gene therapy drugs on the market. Among the products that have been implicitly licensed to carry out clinical trials, the active components mainly include cellular products such as immune cells and stem cells, adeno-associated viruses, adenoviruses and other viral vectors carrying transgenic genes, oncolytic virus products with selective proliferation and oncolytic activity, etc. In recent years, the number of personalized tumor new antigen products began to increase. In addition, there are individual organizations to declare engineering products and combined products.
Combined with the current situation of R & D declaration and the formulation of regulatory regulations / guidelines at home and abroad, in order to improve the efficiency of review, approval and supervision, it is suggested that China's ATMP should be divided into cell therapy drugs and gene therapy drugs. For those drugs that are difficult to be divided into these two categories, consideration can be given to setting a separate category "other" for the time being, and then become a separate category or further subdivision after cognitive maturity. For example, for tissue engineering products and combined products in the classification of EMA and WHO, the number of R & D applications in China is relatively small, and it is suggested to be classified into other categories at this stage. With regard to the emission order of specific categories, we can refer to the international regulatory agencies according to the order of product R & D maturity from high to low and risk grade from low to high, so it is arranged as follows.
The first category: cell therapy drugs.
The second category: gene therapy drugs.
The third category: other.
2. Description and subcategory of cell therapy drugs.
There are differences among different cell therapies in terms of cell source, type and product complexity. For example, cells can be self-renewing stem cells, progenitor cells with a definite direction of differentiation, or terminally differentiated cells that perform specific physiological functions. Cells can come from either autologous, allogeneic or heterologous. In addition, cells may also be genetically modified. These cells can be used alone or in combination with biological macromolecules, small chemical molecules or structural materials. In terms of action mechanism, stem cell therapy drugs can play a role in tissue remodeling by replenishing or replacing damaged cells of patients, and immune cells such as CAR-T can play their biological role by specifically killing tumor cells. Combined with the description of cell therapy drugs by international regulatory agencies, the subcategories of cell therapy drugs need to consider the material basis (active components), action mechanism and functional use. in other words, it is suggested to be divided into non-gene modified cell therapy drugs and gene modified cell therapy drugs.
Combined with the interpretation of cell therapy products by international regulatory agencies, the author describes its pharmacology, immunity, metabolic regulation and cell replacement tissue reconstruction, and makes it clear that it is for the purpose of treating diseases. specific subcategories and common examples are given. At present, in the definition of WHO, the material basis of cell therapy drugs needs to be nucleated cells, but considering that there are erythrocytes and platelets drugs in clinical trials in China, it is not recommended to restrict nucleated cells.
Based on the material basis, drugs with cells as the main active components can be divided into two subcategories: non-gene modified cell products and in vitro gene modified cell products according to whether the cell therapy products are genetically modified or not. Considering that CAR-T and other gene-modified cells generally exert the killing effect of major tumor cells through CAR gene expression combined with target cells, regulatory agencies such as FDA, EMA and WHO generally bring gene-modified cells into the category of gene therapy products. Experts believe that the future development of cell therapy products needs a lot of modification (including genetic modification, combined use of biomaterials, etc.), but its material basis and characteristics are similar to cells, and the final effective drug form is cells. Domestic industry tradition calls it cell therapy products. Therefore, although the classification of these products is different from that of some international regulatory agencies, combined with the current situation of the industry classification of cell products in China, in order to facilitate the management of Chinese regulators, it is suggested that genetically modified cells should be included in the category of cell therapy drugs.
Whether the induced pluripotent stem cell (induced pluripotent stem cell, iPSC) derived cell product belongs to genetically modified cells needs to be determined based on whether the final product has the operation in accordance with the definition of genetic modification. Experts believe that the genetic operation limited to the reprogramming of iPSC seed cells is not genetic modification, but non-genetically modified cell products if it does not involve genetic modification of subsequent cellular drugs.
3. Description and subcategory of gene therapy drugs.
Early gene therapy drugs mainly play a role by introducing functional protein transgenic sequences, and viral vectors and plasmid DNA vectors are commonly used. In recent years, new gene modification tools have emerged one after another, including direct nucleic acid sequences such as microRNA, RNA interference (RNAi) through short hairpin RNA (shRNA), zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) or transcriptional activator-like effect factor nuclease (TALEN), molecular scissors and CRISPR-Cas. These tools may mediate gene sequence repair, amplification or deletion through gene silencing, exon hopping, gene regulation, gene knockout and nucleotide changes. Recently, some genetically modified bacterial carrier products have gradually begun preclinical research and development or clinical trials, and the related bacteria come from Lactococcus, Listeria and Streptococcus, which further expand the types of gene therapy drugs.
In the description of gene therapy drugs by international regulators, the active components of gene therapy drugs are exemplified, and their action mechanism and functional uses are described. Among them, WHO and EMA are clear that the therapeutic effect of gene therapy products is directly related to the recombinant nucleic acid sequence or the gene expression products of the sequence. Combined with the description of international regulatory agencies, the author suggests that the related mechanisms such as specific change of gene sequence / expression and introduction of foreign genes should be emphasized in the description of gene therapy products, and examples of common active components should be given. Combined with the types of gene therapy products currently developed and declared in China, gene therapy products can be further subdivided into viral vector drugs, nucleic acid drugs (DNA, RNA, etc.), gene editing drugs (such as CRISPR-Cas9, etc.), oncolytic microorganisms or other new microbial products.
4. Other classes ATMP.
According to the present situation of the application of innovative biological products in China, there are some products with small declaration quantity and relatively low overall R & D maturity, but considering the development trend of new technology, it is expected to form a class in the future. for example, tumor new antigen products, cell derivatives (such as exocrine) and so on. Therefore, the author sets up the "other" category to bring these products into the category of ATMP, so as to encourage the R & D declaration of innovative products. Because of the strong innovation of this kind of products, it is difficult to draw up a suitable text description, so the author expresses it by citing subcategories. These products mainly include new delivery system drugs (such as cell carriers), personalized target biotherapeutic drugs (such as tumor new antigen drugs), cell derivative drugs (such as exocrine), and tissue engineering drugs with drug properties (such as artificial organs or tissues).
Considering that gene therapy products already include products related to gene delivery tools, but there are still many delivery systems that deliver proteins and small molecules into cells, the authors include these delivery tools in addition to delivering genes, including lipid nanoparticles for delivering proteins, vesicles for delivering small molecules, and so on. Exosomes in cell derivatives can be used not only as drug loading tools, but also as active components, which may wrap proteins or genes. Based on the material basis, it can be further subdivided into natural exocrine drugs, genetically engineered exocrine drugs, exocrine drugs (small molecules). Some vesicle-structured drugs such as viruses and bacteria can also be secreted by cells, such as virus-like particles, which are seldom declared at present. When they arise, we can consider whether they can be included in the subclass of cell derivatives through specific analysis of specific problems. In addition, a large number of declared products include a class of personalized tumor new antigen products, the active components of which may include genetically modified cells, DNA, RNA and even peptides. Based on the material basis, it is difficult to incorporate such products into cell or gene therapy drugs, so consider placing them in other categories.
At present, cell therapy drugs are mainly developed with single cell type as the main active ingredient, and gradually there are products combining multiple cell types for clinical trials. Some products such as liver organs have been used in clinical research in China, and some tissue engineering products such as brain, gastrointestinal, pancreatic organs and artificial cornea are also in the process of rapid development. Combined with the current situation of research and development, the author considers to include artificial tissues and organ drugs with drug properties into other categories. For xenotransplantation products, there is no such drug declaration in China, and experts suggest that the inclusion of xenotransplantation should not be considered for the time being. Combined with the current situation of international development, if there is a subsequent declaration of genetically modified animal tissues or organs in China, considering that such products involve animal quarantine and public health prevention and control of zoonosis, joint supervision may be required with other regulatory agencies.
5. Boundary case.
There may be a variety of complex situations in the actual process of confirming whether a product belongs to ATMP and classification. The same product can be divided into different categories according to its material basis and mechanism of action. For example, the cellular composition of islet corpuscles includes a variety of cell types, such as islet α cells, islet β cells and so on. According to the material basis, it can be classified as cell therapy drugs, and considering the integrity of its basement membrane, it can also be classified as organ / tissue engineering drugs in other categories. In addition, the mechanism of action of some products is not clear or there are a variety of mechanisms, such as gene modified organ products, there are gene modification related biological activity and tissue remodeling function. There may also be different classifications of these products (genetically modified cell subclasses in cell therapy drugs, or tissue engineering drugs), so it is necessary to analyze the specific situation and, on the basis of accumulated experience and investigation, consider to develop further classification principles according to risks and mechanisms of action.
Summary.
ATMP is the most potential and promising development direction in the field of biomedicine at present, and it occupies an important part of international competition and national strategic planning. The guidance of clinical value, the policy support of the whole industry chain, the drive of cutting-edge technological innovation, continuous capital enrichment and scientific strict and prudent supervision and escort will jointly promote the high-quality development of China's advanced treatment industry and cultivate the new productivity of biomedicine. Meet the unmet clinical needs of the people in a timely manner.
At present, the bio-pharmaceutical industry as a whole has encountered a cold winter of capital, and the promotion of product pipelines has been blocked. At present, the number of listed products is limited, and the pricing of products is high, medical insurance is not yet fully covered, and the market capacity to pay is insufficient. There is still a big gap in drug supply, accessibility and affordability. Therefore, regulators should pay more attention and support to the research and development of such products, and provide more clear regulatory policies and incentives.
The suggestions on the classification and definition of ATMP provided in this paper, the overall classification framework and logic are in line with the classification system of major international regulatory bodies, and are expected to provide reference for the formulation of supporting policies related to follow-up regulatory classification, and guide and improve the corresponding technical guidelines, standard system and international regulatory coordination, so as to further enhance the regulatory effectiveness of ATMP and accelerate the R & D declaration, approval and listing of related products. To help meet the unmet clinical needs of the people.