
Source: Bio-protocol
On November 20, 2023, Bio-protocol published online in the journal "Efficient Differentiation of Human Induced" by Nazir M. Khan and Hicham Drissi of Emory University, USA Pluripotent Stem Cell (hiPSC)-Derived Mesenchymal Progenitors Into Adipocytes and Osteoblasts.
DOI:10.21769/BioProtoc.4885
Key words: osteoblastic adipogenesis hiPSC cell derived mesenchymal progenitor cell three-line differentiation regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine (Regenerative medicine) refers to the use of biological and engineering theoretical methods to create lost or functionally damaged tissues and organs, so that they have the structure and function of normal tissues and organs.
一、Background introduction
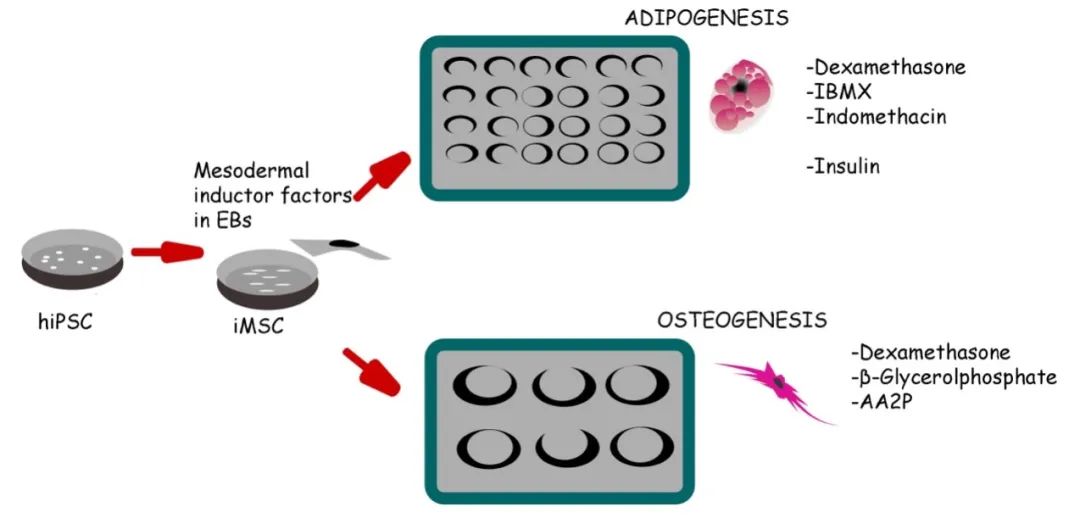
In the field of regenerative medicine, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have the ability to self-renew and regenerate in adult tissues, but their potential as a therapeutic means needs to be further developed due to differences in donor age, tissue selection and isolation methods. The International Society of Cell Therapy has proposed a series of criteria for identifying MSCs, including adhesion to plastics under standard culture conditions and expression of specific surface markers. Recently, MSCs have received attention for their immunomodulatory properties, intrinsic regenerative capacity, and multidirectional differentiation potential. At the same time, MSCs (i.e., iMSCs) derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) present a new research direction. iMSCs provide a unique platform for the development of differentiation methods targeting fat cells, cartilage and bone by mimicking the molecular cues present in embryos. In addition, iMSCs demonstrated faster proliferation capacity and limited adipogenesis capacity compared to bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs). This paper presents a detailed method for differentiation of osteoblasts and adipocytes from human iPSCs, which is intended to be achieved through mesenchymat-like progenitor cell intermediates. This approach provides a new perspective for understanding the differentiation potential of HiPSC-derived iMSCs and their application in disease modeling and regenerative therapy.
二、Method highlights
For iMSCs derived from hiPSCs, this paper proposed an optimized experimental protocol to enhance the efficiency and repeatability of cell differentiation.
三、Potential application
Regenerative medicine research
This experimental method provides an important tool for in-depth understanding of the mechanism of cell differentiation and tissue regeneration, and promotes the development of regenerative medicine and cell therapy.
四、Repeatability verification
The reproducibility of this method has been verified by the team of Nazir M. Khan and Hicham Drissi at Emory University, USA. The experimental data and results are published in Elife, DOI:10.7554/eLife.83138.