
Source: International Stem Cell Research
Stem cell therapy is a worldwide topic in medical science. Stem cell research originated in Europe, including Switzerland, Germany, Eastern Europe and other places have decades of history and rich cases of regenerative medicine and stem cell research. In Asia, Japan's stem cell research started later than Europe, but the development rate is faster, since the first stem cell product for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease - Temcell was approved in 2015, it has been eight years. So what is the current status of stem cell therapy in Japan? What products have been approved?
Development and current status of stem cell therapy in Japan

In Japan, stem cell therapies related to research and development (commonly referred to as regenerative medicine) have been led by the Japanese government.
2010
In 2010, Japan revised the Guidelines for Clinical Research Using Human Stem Cells, expanding the scope of stem cell clinical research to include embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
2011
In 2011, Japan launched the "Highway Program to Achieve Regenerative Medicine" and strengthened its support for preclinical research on stem cells, playing an important role in facilitating the transition of stem cells to clinical applications. Of the 18 projects initially selected for the program, 15 have now been announced for clinical implementation.
2012
In 2012, Professor Shinya Yamanaka won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his research on "somatic cell reprogramming technology." This also led Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe to have great expectations for induced pluripotent stem cell research, and pledged to invest 110 billion yen (about $1 billion) over the next decade to support the development of regenerative medicine.
2014
At the end of 2014, Japan began to implement the Regenerative Medicine Safety Law and the Drugs and Medical Devices Law.
According to the Medical Safety Law on Regenerative Medicine, regenerative medicine is classified into three categories according to the treatment risk: Type I regenerative medicine (including induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem cells, and allogeneic stem cells), Type II regenerative medicine (including autologous stem cells, such as autologous fat stem cells), and Type III regenerative medicine (such as dendritic cells, NK cells, and T cells).
The Drugs and Medical Devices Act requires institutions applying for stem cell therapy to provide efficacy data from small-sample clinical trials. At this point, the stem cell dual-track regulatory system has gradually improved.
2023
As of 2023, the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has approved more than 10 stem cell products, including bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, adipose mesenchymal stem cells, and corneal epithelial stem cells. There are thousands of clinical research projects in areas such as human kidney tissue cultivation and "in vitro ovary" reconstruction. In addition to the research of stem cells themselves, they have also been continuously explored in the field of stem cell derivatives such as stem cell supernatants and exosomes to meet the needs of patients for cosmetic anti-aging and treatment of chronic diseases. The favorable policy has also attracted traditional industry giants such as Ledun and Fujifilm to join the army of commercialization of stem cell products through mergers and acquisitions, and further promoted the development of stem cells in Japan.
What are stem cells for?
As a new type of therapy, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has only approved its use in certain blood and immune system diseases. But researchers are also exploring other applications for stem cells, Such as chronic pain, anti-aging, enhance the body's immunity, treatment of osteoarthropathy (such as arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis), neurological diseases (such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, spinal cord injury, stroke sequelae), cardiovascular diseases (such as hypertension, cardiomyopathy), metabolic diseases (such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, diabetic foot), autoimmune diseases Diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, Sjogren's syndrome, atopic dermatitis), digestive diseases (such as fatty liver, alcoholic liver) and so on. Stem cell therapy provides a new therapeutic idea for some chronic and refractory diseases that have reached the limit of traditional treatment.
What are the approved products of stem cells?
Table 1 Approved products of Japanese stem cells
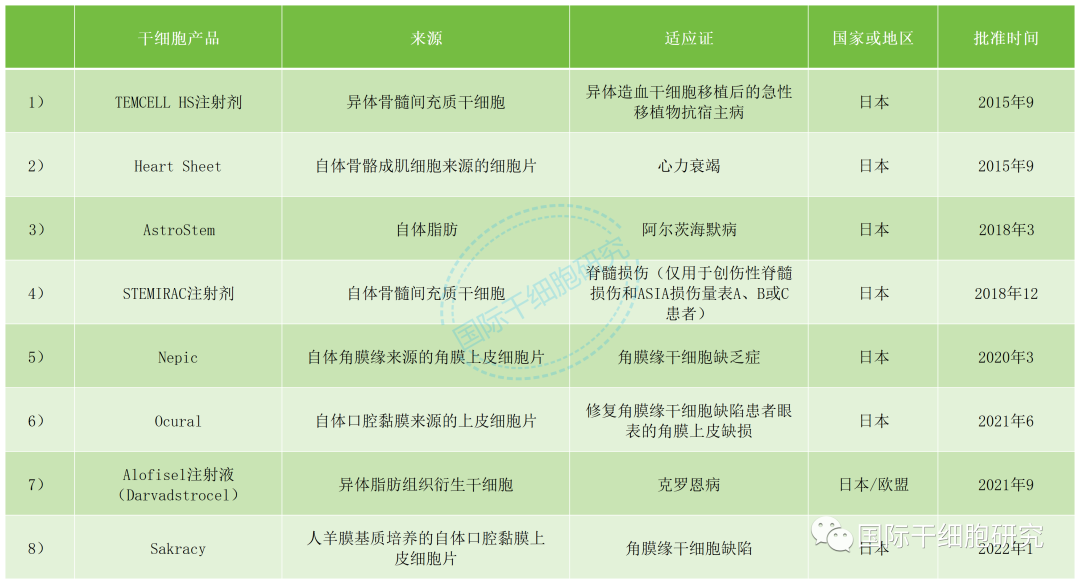
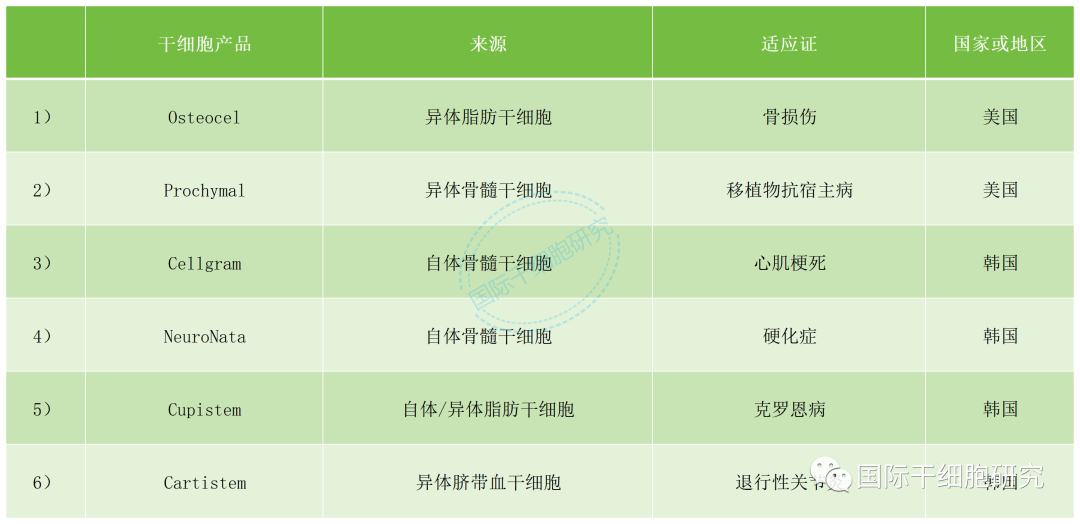
Table 2 Products approved in other countries
What is unique about Japanese stem cells and what is worth learning from them?
Stem cells as an emerging cutting-edge technology, its extraction, culture, storage, etc., have strict requirements, any link problems, may affect the final effect of stem cells. So, as the "leader" of stem cell technology in Asia, what is worth learning from Japan?
1、Strict supervision
Supervision of stem cell therapy: Many factors such as the source of stem cells' donors, culture environment, survival quantity, proliferation, preparation conditions, etc., will affect the quality of stem cells and ultimately affect the therapeutic effect of stem cells. But the quality of stem cells is difficult for the average consumer to tell with the naked eye. In order to avoid the chaos of stem cells, Japan has adopted a sound dual-track supervision model of "medical technology and new drugs", and promulgated the "Regenerative Medicine Safety Law", "Drugs and Medical Devices Law" and other relevant laws for supervision.
Supervision of stem cell culture and storage: Stem cells are delicate and need to be frozen in a low temperature liquid nitrogen tank at -196℃ to maintain their activity; In addition, cell culture should also adopt a strict quality management system, including the virus and other related checks when the cells are stored; In the process of culture, it was carried out in a serum-free culture base to ensure its safety. Japan regulates the cultivation and storage of stem cells in accordance with the Law on Ensuring the safety of regenerative Medicine approved by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
2、Strong research team
Many top universities in Japan (including Kyoto University, Tohoku University, Tokyo University of Science, Kyushu University, etc.) are involved in stem cell research, among which Professor Shinya Yamanaka, who won the Nobel Prize, worked at Kyoto University.
3、Be covered by medical insurance
Japan has included regenerative medicine products in its health insurance coverage, including cell transplantation therapy for repairing and restoring damaged skin, articular cartilage and stroke, allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells for graft-versus-host disease, and CAR T cell therapy. By requiring patients treated with regenerative medicine products to pay only 30 percent of the cost of treatment, this measure greatly reduces the burden on patients and increases the availability of stem cell products.
Sum up
"If life has a weight and measure, it must be the length of the cell", in recent years, with the continuous development of regenerative medicine, regenerative medical products represented by stem cells have gradually become the "must-have" of cutting-edge science and technology in various countries. The United States, Japan, South Korea, and the European Union are in a leading position in the field of stem cell research, and a number of products have been approved for market. At present, there are still many constraints in our country, but with the support of relevant policies such as the 13th Five-Year Plan and the 14th Five-Year Plan, the development of stem cells in our country is also good in the long run. Xiaobian also hopes that the supervision of stem cells can be improved in the future, and more patients can be benefited in the future!