
Source: Yao Du
On January 9, 2024, Eisai (China) Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. announced that Lecanemab, a breakthrough targeted drug for Alzheimer's Disease (AD), was approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and officially entered China. It is used to treat mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia caused by Alzheimer's.
Lecanemab is currently the first and only fully approved drug that delays AD progression and reduces the rate of cognitive function decline by clearing the mechanism of β-amyloid Protein (Aβ), and has been listed as one of the top ten scientific breakthroughs in 2023 by the American journal Science. With full approval in the United States in July 2023 and approval in Japan in September 2023, China is the third country to approve lencanetzumab for marketing. According to Eisai (China), the drug is expected to be launched in China in mid-July 2024.
This news caused great concern in the medical industry, on the one hand, due to the complex pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and the very strict clinical trial review procedure, its new drug development has the highest failure rate recognized by the industry of 99.6%, known as the "death valley" of drug development, Roche, Merck, Astrazeneca and other well-known drug companies have broken or lost. On the other hand, there are only two types of drugs approved globally for the treatment of AD, which are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Donepezil, cabalatine, galantamine, etc.) and NMDA receptor antagonists (Memantine), and there is no beta-amyloid antibody drug such as Lecanemab. For the world's first Alzheimer's targeted drug approved to enter China, this article briefly analyzes and introduces the origin, mechanism of action, clinical effects and other aspects of lencanizumab, in order to lead readers to a more comprehensive understanding of this drug.
01 Birth of Lecanemab
The man behind Lecanemab is Lars Lannfelt, a Swedish professor of medicine, and it could be argued that without him there would be no follow-up story.
Professor Lars Lannfelt made his name in the field of dementia research in the 1990s with the discovery of the Aβ-Arctic mutation (APPE693G, which leads to increased production of Aβ oligomers/primary fibril and accelerated fibril formation, causing early-onset AD). At that time, scientists believed that amyloid plaques were the main cause of Alzheimer's disease, while Professor Lars Lannfelt believed that soluble Aβ aggregates composed of oligomers and fibril in the brain were the real cause of AD, and used this as A starting point to explore the treatment of AD. In mid-2005, BioArctic, A company co-founded by Professor Lars Lannfelt, developed mAb158 (a mouse precursor to BAN2401/Lecanemab), which targets Aβ fibrils and is a precursor to Lecanemab.
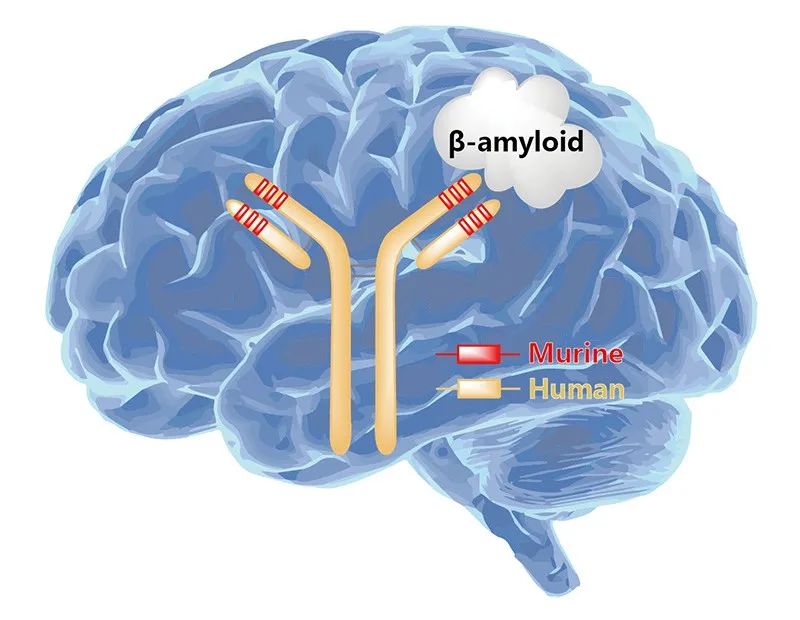
Figure 1. Action of Lecanemab on brain Aβ protein
That same year, BioArctic and Eisai entered into a research collaboration on disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer's disease, with a focus on the development of Lecanemab. In 2007, Eisai and BioArctic signed an agreement to acquire global R&D, manufacturing and marketing rights for Lecanemab for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Since then, after 20 years of research and development, lencanizumab finally received full FDA approval for the treatment of early Alzheimer's disease in July 2023.
02 Action mechanism
Alzheimer's disease is a kind of neurodegenerative disease with insidious onset and progressive development. The main clinical manifestations are cognitive decline, impaired ability of daily living and mental behavior symptoms. The pathogenesis of AD is complex and diverse, and there are many hypotheses but no specific conclusions, mainly including amyloid cascade hypothesis, cholinergic injury hypothesis and Tau protein abnormal phosphorylation hypothesis.
Amyloid plaques, as one of the typical pathological features of Alzheimer's disease, are mainly composed of Aβ. According to the hypothesis of Amyloid cascade, after synthesis of Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) in normal human body, it can be hydrolyzed through non-starch source pathway and starch source pathway, in which the starch source pathway mainly relies on β and γ secretory enzyme cleavage. However, with age or abnormal function of β and γ secreting enzymes, Aβ40 and Aβ42 monomers will be produced, and the monomers will further oligomerize and aggregate to form plaques, blocking ion channels, increasing mitochondrial oxidative stress, thus destroying healthy neurons, and ultimately leading to loss of neuron function (Figure 2).
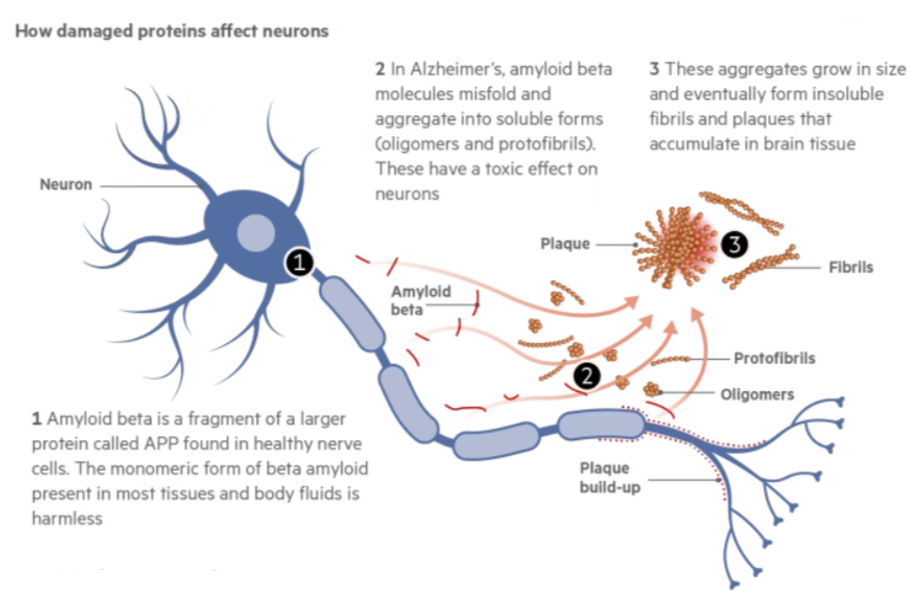
Figure 2. Effect of Aβ protein on neurons
Lecanemab, as A recombinant human immunoglobulin IgG1 monoclonal antibody, has A high affinity for soluble Aβ protein aggregates. It is precisely through targeted binding to the N terminal of Aβ protein that Lecanemab promotes the removal of abnormal accumulation of Aβ protein, thereby reducing the formation of amyloid plaques and alleviating the progression of Alzheimer's disease. It is important to emphasize that Lecanemab can only slow down the process of cognitive decline, not reverse it, that is, there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease.
03 Clinical study results
Clinically, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is used to detect the changes of brain Aβ plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Combined with Alzheimer's Disease Composite Score (ADCOMS) and Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Self-Scale (ADCOMS), ADAS-Cog, Clinical Dementia Rating-Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB) and other scale scoring methods.
In the Phase IIb clinical study of lencanizumab, 856 patients with early-stage AD were randomly assigned to five dose groups of 2.5mg/kg every 2 weeks, 5mg/kg every month, 5mg/kg every 2 weeks, 10mg/kg every month, and 10mg/kg every 2 weeks. Initially at the 12-month mark, lencanetzumab failed to meet its primary clinical endpoint and was close to a "death sentence." But at the 18-month mark, there is a significant remission in Alzheimer's disease progression. Clinical results showed that lencanizumab was dose-dependent in reducing Aβ plaques. In the highest dose group (10mg/kg every 2 weeks), patients' amyloid decreased by an average of nearly 70 units as measured by PET, achieving statistical significance (P<0.0001).
In addition, at 18 months, 81% of patients changed their status from amyloid-positive to negative (P<0.0001). Patients also experienced a 30% reduction in clinical decline (based on the ADCOMS score) compared with placebo controls (p=0.034).
In a multicenter, double-blind Phase III trial conducted in 2022, 1795 patients aged 50 to 90 years with early-stage AD were divided into a lancanizumab treatment group (898 cases) and a control group (897 cases) and received intravenous administration of 10 mg/kg once every 2 weeks for 18 months. Clinical results showed that lencanizumab slowed the progression of cognitive dysfunction by 27% in patients with early AD compared to controls:
The CDR-SB scores of the two groups were 1.21 and 1.66, respectively (difference 0.45, 95%CI -0.67 ~-0.23, P < 0.001) (Figure 3).
The ADCOMS scores of the two groups were 0.164 and 0.214, respectively (difference -0.050, 95%CI -0.074 ~-0.027, P < 0.001).
For Aβ plaques, baseline levels in the treatment and control groups were 77.92 centloids and 75.03 centloids, respectively, and after 18 months of treatment, Amyloid levels in the two groups were -55.48 centloids and 3.64 centloids, respectively (difference -59.12 centloids, 95%CI -62.64-55.60, P < 0.001), and the results were also statistically significant. Lencanizumab showed clear therapeutic advantages, both in slowing cognitive dysfunction and clearing Aβ protein. In addition, in cerebrospinal fluid subgroups and plasma analyses of subjects, markers of Aβ protein, Tau protein, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation were reduced to A greater extent in the lencanizumab group compared to the control group.
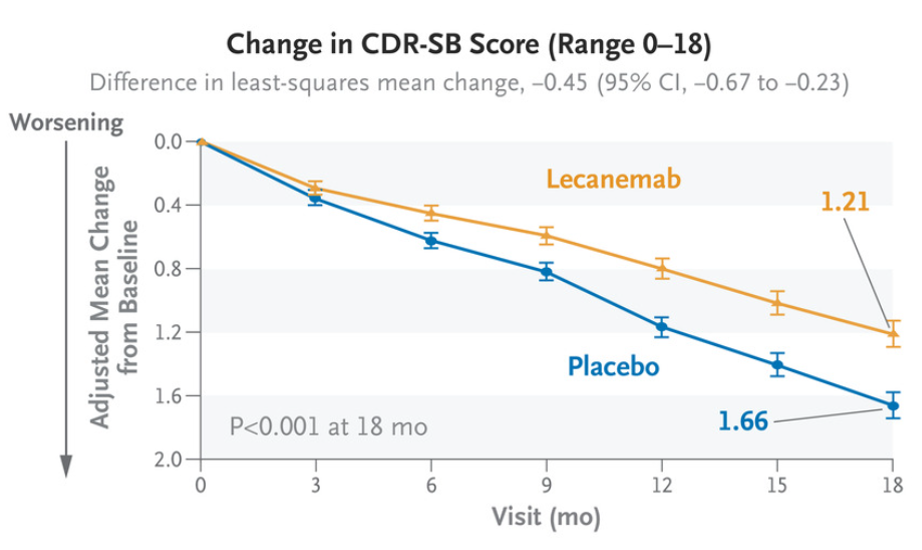 Figure 3. Changes of CDR-SB in treatment and control groups over treatment time
Figure 3. Changes of CDR-SB in treatment and control groups over treatment time
The risk to be aware of is that brain swelling and bleeding in the brain are common side effects of lencanetzumab. Regarding brain swelling, clinical studies showed that 12.6% of patients in the treatment group experienced brain swelling compared to 1.7% in the control group, and patients with AD who received lencanizumab had a higher risk of brain swelling. The main symptoms are headache, visual impairment and confusion. In the course of treatment, most patients had mild to moderate brain swelling, which mostly occurred in the first 3 months of treatment, and usually could be significantly relieved within 4 months, and a few patients had obvious brain swelling symptoms. For intracerebral hemorrhage, the study showed that 17.3% of patients receiving lenkanizumab experienced intracerebral hemorrhage, compared with 9% in the placebo group, with dizziness being the most common symptom.
定价方面,仑卡奈单抗说明书的推荐剂量为10mg/kg,每两周使用一次。如果按此计算,一位60kg的患者年均治疗费用约为18万元,比此前海南博鳌乐城国际医疗旅游先行区(2023年10月,仑卡奈单抗通过海南省药品监督管理局审核落地海南博鳌先行先试区)的定价减少约8万元。最新的定价大致与美国市场定价相同。具体花费会根据患者体重的差异而浮动。
04 The layout of many domestic pharmaceutical companies
According to the Alzheimer's Association International website, there are currently more than 55.2 million people with Alzheimer's disease worldwide, with an average of one new person suffering from Alzheimer's disease every three seconds. Due to its large population base, China accounts for more Alzheimer's patients in the world. According to the statistics of the National Health Commission, there will be about 10 million Alzheimer's patients in the population aged 60 and above in China in 2022.
In view of the huge market demand, even if it is a tough bone, there are still many challengers, according to the Galaxy Securities research report in November 2023, a total of 34 new drugs for Alzheimer's disease in China have entered the clinical stage, including Simcere Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.,Hisun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tonghua Golden-Horse Pharmaceutical Industey Co., Ltd. and so on.
Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.
Among them, the most concerned is Hengrui medicine independent research and development of humanized anti-Aβ antibody SHR-1707, the drug is expected to become the first self-developed anti-Aβ monoclonal antibody, the current study has completed the first patient enrollment and administration, in November 2023 Hengrui Medicine said on the public platform, the overall performance of SHR-1707 research results in line with expectations.
Simcere Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
In 2021, Simcere Pharmaceutical and Vivoryon reached a cooperation of more than 500 million US dollars to introduce the rights and interests of Alzheimer's treatment drugs for amyloid N3pE (pGlu-Abeta) with neurotoxicity, becoming the first company to introduce AD innovative drug pipeline in China.
Tonghua Golden-Horse Pharmaceutical Industey Co., Ltd.
Tonghua Jinma layout is a new acetylcholinesterase inhibitor "amber octahydroaminoacridine tablet", which is used to treat mild and moderate AD. On September 20, 2023, the Company announced that the Phase III clinical trial of "Aminoacridine tablets in amber" was successful, achieving the primary clinical trial endpoint.
Brief summary
Although the pathogenic mechanism of Alzheimer's is not clear, there is still a lot of room for clinical treatment. One is to focus on another pathological protein, Tau protein; The second is to develop drugs for neuroinflammation and vascular injury that aggravate the pathological changes of AD; The third is to learn from the tumor immune "cocktail" therapy, the future AD treatment can be more diversified, and multiple measures can be combined for different targets.
The successful release of Lecanemab is undoubtedly a major breakthrough in the field, whether it is a new dawn for pharmaceutical research and development companies or AD patients, I believe that in the near future, there must be a drug or therapy that can truly cure Alzheimer's.