
Source: International Stem Cell Research
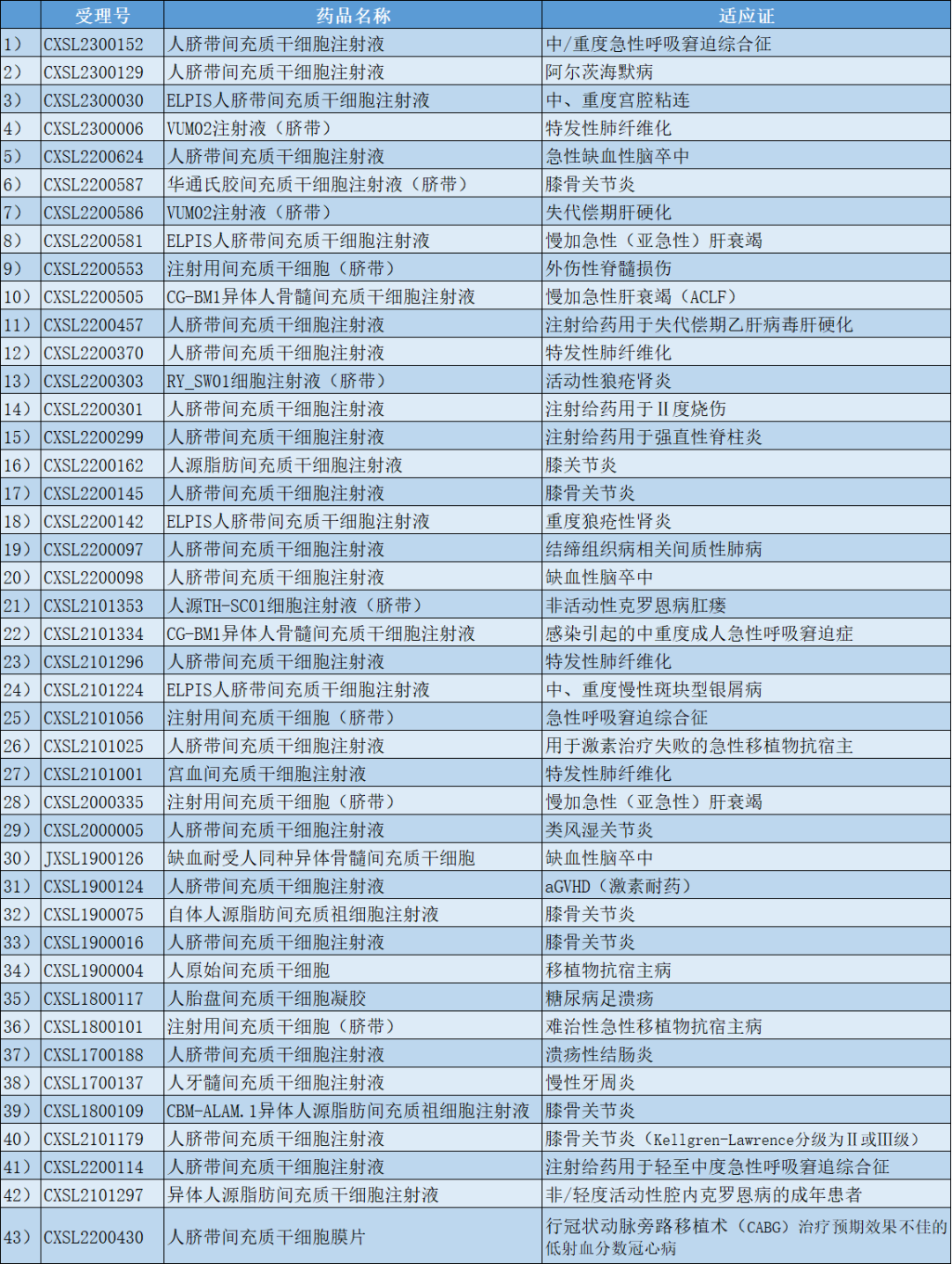
As of May 2023, a total of 43 mesenchymal stem cell drug clinical trials in China have been acquiesced by the Drug Review Center of the State Drug Administration.
According to the statistics of Clinical trials database, as of December 2022, there have been 1,495 clinical studies on mesenchymal stem cells registered worldwide, mainly involving respiratory diseases, reproductive system diseases, autoimmune diseases, metabolic diseases, osteoarthropathy, liver disease, eye diseases and other fields.
New mesenchymal stem cell drugs
Table 1 mesenchymal stem cell drugs already on the market
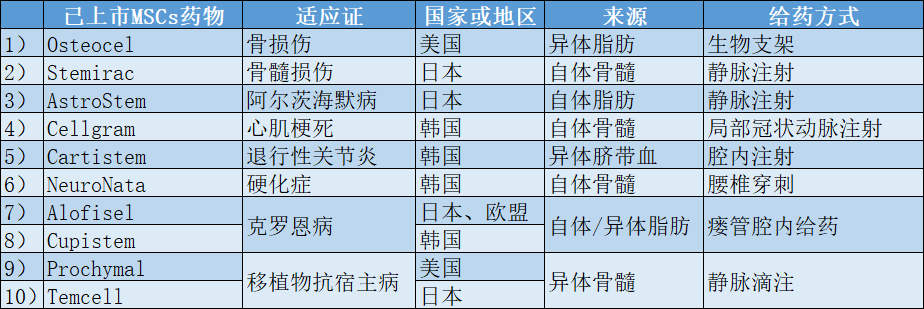
Table 2 Summary of implied approval for domestic mesenchymal stem cell drug clinical trials (as of May 2023)
What are mesenchymal stem cells?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from mesoderm, widely found in bone marrow, placenta, umbilical cord, cord blood and other tissues. Compared with other stem cells, MSCS have stronger proliferation and differentiation potential, and can differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes and chondrocytes, and secrete anti-inflammatory factors and neuroprotective factors. It plays multiple roles such as immune regulation, vascular regeneration and tissue repair, and is an important member of the stem cell family.
When the body tissue injury or inflammatory cell infiltration occurs, after exogenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells, the cells can return to the lesion site, and interact with a variety of cells in the body, restore the normal physiological function of the body, maintain the homeostasis of the body microenvironment, and repair the diseased tissues and organs.
What are mesenchymal stem cells for?
Mesenchymal stem cells have the potential to improve cardiovascular diseases, improve a variety of nerve functions, reduce the degeneration of articular cartilage, etc., and have broad potential in osteoarthropathy, nervous system diseases, autoimmune diseases, metabolic diseases and many other fields.
01 Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
Alzheimer's disease is A chronic neurodegenerative disease, the exact pathogenesis of which is still not very clear, may be associated with the deposition of harmful chemicals (such as Aβ plaque), intracellular NFT, etc., resulting in abnormal connections between neurons and synapses between neurons, thus triggering dysfunction of information transmission between neurons. At present, drug treatment is mainly used, but drug treatment can only relieve early symptoms and cannot prevent the disease from continuing to progress.
Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells can reduce the accumulation of Aβ and phosphorylated Tau protein, thereby helping to improve spatial memory ability and cognitive function. In addition, astrocytes and microglia play an important role as the brain's main immune cells in neuroinflammation, and transferring a gene for MSCS can improve neuroinflammation by regulating astrocytes and microglia, which can greatly alleviate Alzheimer's disease.
02 Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative movement disorder caused by the gradual loss of dopamine neurons in the midbrain. At present, drugs and surgery are the main treatments, but there is no cure for the disease, and stem cell therapy is expected to become a new breakthrough in treatment.
Studies have shown that the secretion set of mesenchymal stem cells includes a variety of cytokines and extracellular vesicles, vesicles contain a variety of proteins, DNA, RNA, etc., which are involved in the regulation of target cell signaling pathways, and have the potential of transdifferentiation, which can form neurogenic potential and transdifferentiation into neurospheres under certain circumstances, and inhibit the continuous progression of Parkinson's disease from the etiological level.
03 Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a widespread, generally age-related, systemic bone disease characterized by a loss of bone mass associated with an imbalance between bone formation by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts, ultimately leading to bone weakness and an increased risk of fracture.
Studies have shown that during the adult years, when MSCS are stimulated by mechanical load, they will produce more reactive oxygen species, resulting in reduced differentiation ability and affecting bone function. Therefore, the osteogenic differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cells plays a key role in age-related osteoporosis. After transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells, bone quality can be improved by increasing bone density, thus reducing the probability of fracture, and autologous or allogeneic transplantation has the effect of treating osteoporosis.
04 Cardiovascular disease
It includes rheumatic heart disease and tuberculous pericarditis caused by infectious factors, as well as hypertension, myocardial infarction, stroke and peripheral artery disease caused by non-infectious factors.
Studies have shown that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCS) can improve cardiac function by differentiating into endothelial cells, which can repair the damaged cardiovascular system. In addition, it can also enhance the ability of new blood vessel formation through the paracrine mechanism, which is very promising in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Brief summary
Mesenchymal stem cells have the biological characteristics of self-renewal, multidirectional differentiation potential and immune regulation, which bring the hope of curing some refractory diseases, and have good clinical safety, and have irreplaceable advantages in clinical application.
With the introduction of policies such as "Measures for the Management of Stem Cell Clinical Research (trial)", "Guiding Principles for the research and Evaluation of cell therapy Products (trial)" and "Guiding Principles for the quality control and preclinical research of stem cell preparations (trial)", the clinical transformation of stem cells in China has entered a stage of orderly development, and it is expected that more new stem cell drugs can be developed in the future to benefit more patients.