
Source: Molecular biomedical
Stem cells and their applications
Stem cells are a class of primitive cells with the potential for self-replication and multidirection differentiation, which can differentiate into various types of cells to repair or replace damaged or diseased tissues. Stem cells are widely used in healthcare, mainly in the following aspects:
1. Treatment of major diseases: Stem cells play a huge role in many major disease areas, such as diabetes, stroke, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and lymphoma. In addition, the emergence of stem cells provides the possibility for the treatment of cancer. For example, mesenchymal stem cells can be used as the carrier of cancer treatment drugs, which helps drugs to be more accurate treatment, and mesenchymal stem cells can regulate the immune environment and improve immune function to fight cancer.
2. Cosmetic application: Stem cells have great potential in the field of cosmetic surgery, which can effectively repair damaged muscle tissue cells, improve the living environment of body cells, and effectively resist aging
3. Improve infertility: stem cells can enter the body tissue to effectively repair, for infertility is mostly due to damage to the endometrial defect, resulting in abortion, stem cells can repair
4. Tissue repair and regeneration: stem cells have the potential of self-replication and multi-differentiation, and can regenerate various tissues of the human body, so they have certain clinical potential in tissue repair and regeneration, especially in fracture healing, cartilage healing and post-traumatic inflammation.
In general, the role of stem cells in healthcare is mainly reflected in repairing and replacing damaged or diseased tissues, treating major diseases, improving infertility conditions, and promoting tissue repair and regeneration. However, stem cell therapy is still in the research stage and has not yet fully realized large-scale clinical application, so it needs to be treated with caution in practice.
Stem cells in healthcare
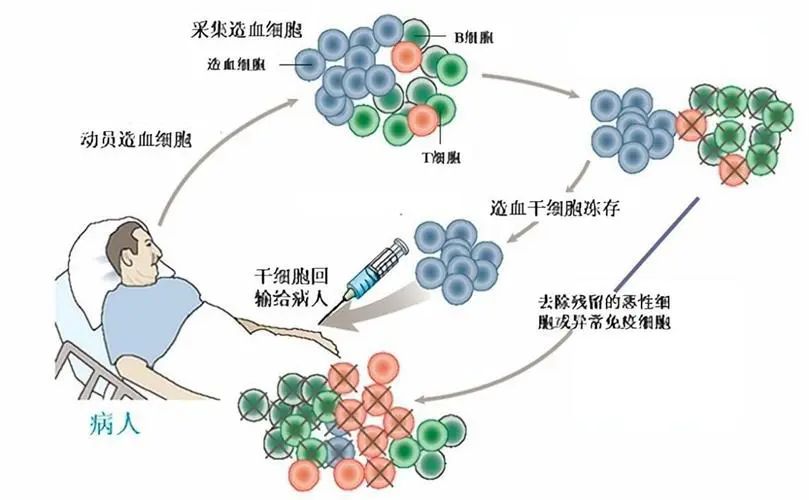
Stem cells play an important role in healthcare, and their multidirectional differentiation ability and unlimited division and proliferation make them a potential stock for the treatment of various diseases. Among them, the commonly used stem cells are hematopoietic stem cells, which can be used to treat blood system diseases and some tumor diseases. For example, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can eliminate the original diseased stem cells in the patient's body, eliminate the original hematopoietic immune system, and help extend survival time and improve discomfort symptoms.

In addition, umbilical cord derived stem cells have also been used in clinical research, they can solve the skin, bone, heart muscle, lung, liver, kidney, cornea, endometrium, ovary, breast and other different tissues and organs injury and difficult diseases.
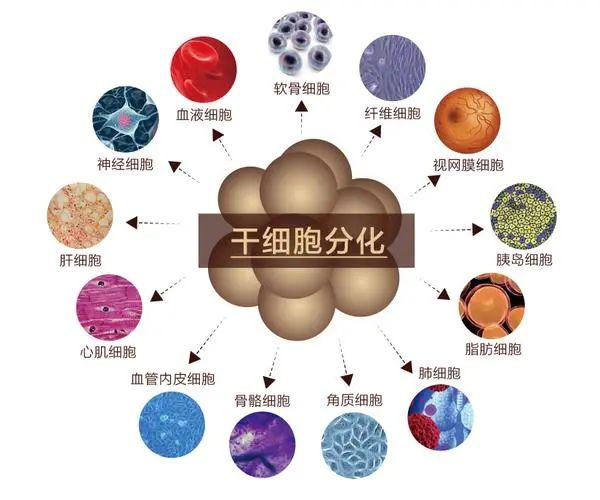
To be specific, Stem cells can enhance the body's immune system, adjust the growth factor index, promote rapid wound healing to avoid scars, promote the regeneration of organ tissue cells, rejuvenate organs, delay organ aging, improve sleep quality, improve sub-health, protect the liver to treat liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, promote metabolism, enhance physical strength and energy to make the body energetic, promote cardiomyocyte growth and improve the heart Functional endurance Prevent heart disease and stroke, stabilize blood pressure, balance cholesterol, improve skin and problem skin, restore skin luster, smooth and elastic, reduce wrinkles, improve facial rejuvenation, enhance sexual ability, improve sexual life quality, improve motor system ability, improve osteoporosis, waist and leg pain, restore nervous system function, improve memory, prevent Parkinson's disease and many other diseases.
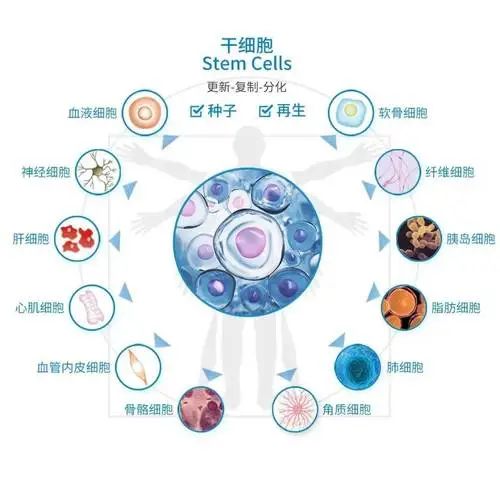
In short, stem cell therapy is a medical method with wide application prospect. With the continuous development of medical technology and the deepening of people's understanding of stem cells, it is believed that more research and application results will emerge in the future and make greater contributions to human health.