
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are a kind of adult stem cells with the ability of self-renewal, multi-lineage differentiation, tissue regeneration and immunomodulation. they have the advantages of easy isolation and easy acquisition. they have attracted wide attention since they were discovered in 1968, and have become an ideal source for different clinical applications.
The origin and differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) come from a variety of sources, including:
1. Bone marrow is the most commonly used source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): bone marrow is the spongy tissue in the bone, containing immature cells, including mesenchymal stem cells.
These cells can be collected through a procedure called bone marrow aspiration, which is relatively simple and safe.
2. Adipose tissue (Fat Tissue): mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be isolated from adipose tissue, which is the tissue that stores fat in the body.
Adipose tissue can be obtained by liposuction, which uses a hollow stainless steel tube to remove fat from the body.
3. Umbilical cord tissue: mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be obtained from umbilical cord tissue, which is the tissue connecting fetus and placenta.
Cells can be collected and stored at birth for future use.
4. Peripheral blood: there are a small amount of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in the peripheral blood of healthy adults.
These cells can be collected through a procedure called single sampling, which is similar to blood donation.
5. Placental tissue: mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be obtained from placental tissue.
Cells can be collected and stored at birth for future use.
6. Synovial fluid: there are a few mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in synovial fluid.
Synovial fluid can be obtained by joint puncture, which is a relatively simple and safe operation.
7. Dental pulp: there are a small number of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in dental pulp.
Dental pulp can be obtained by a procedure called apical resection, which is a surgical procedure to remove the apical of a tooth.
The youthful nature of these cells gives them great potential to transform into any type of cell needed in the body.
Young cells tend to replicate faster, and mesenchymal stem cells can not only differentiate into other cell types, but also enhance the healing effect of the body through proliferation. The researchers also found that the efficacy of stem cells is related to their age, which makes umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells one of the most capable cells. It is worth noting that the isolation and expansion of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) from different sources may be different and have other characteristics.
In addition, isolation of MSC from certain locations, such as peripheral blood and synovial fluid, may be more challenging and less efficient than mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue or umbilical cord tissue.
According to a peer-reviewed study published in the journal Stem Cell Review and report, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have been shown to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (osteoblasts), chondrocytes, adipocytes, muscle cells, nerve cells, hepatocytes, pancreatic cells, cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells (vascular cells), and epithelial cells (cells arranged on the surface).
There are 87 new drugs accepted by mesenchymal stem cells in China.
According to the information disclosure of the latest CDE official website, 87 new drugs with "mesenchymal stem cells" in their names have been accepted as of May 6, 2024.
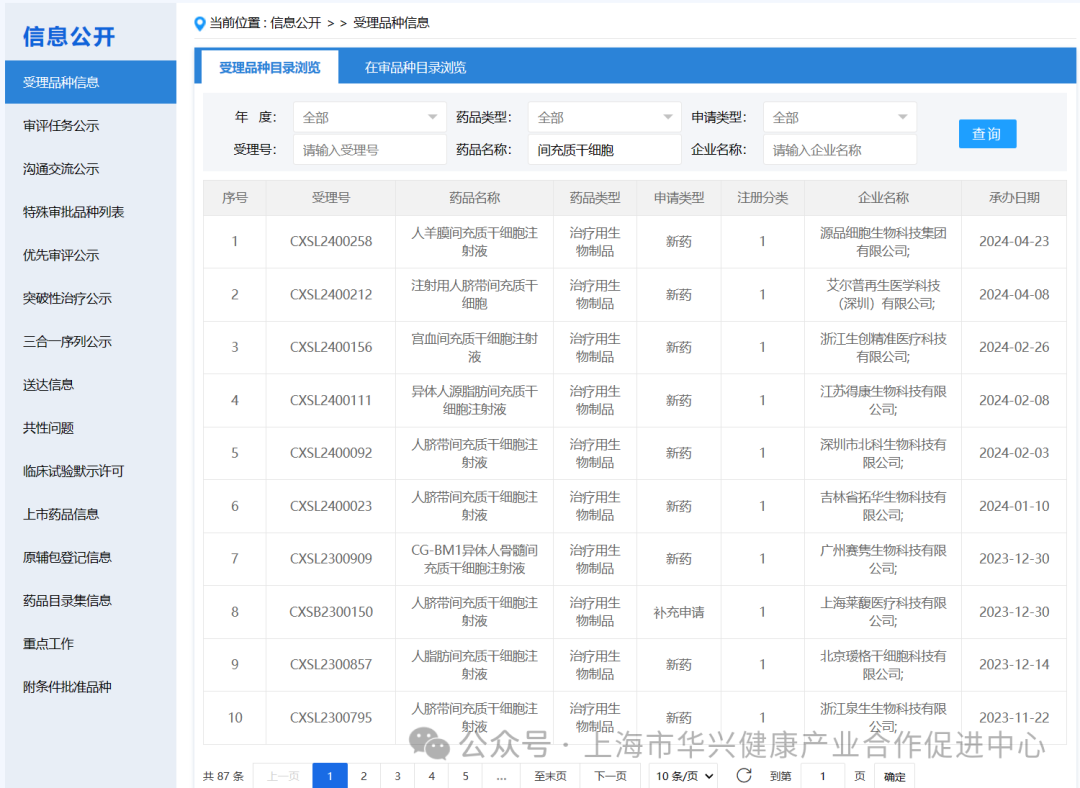
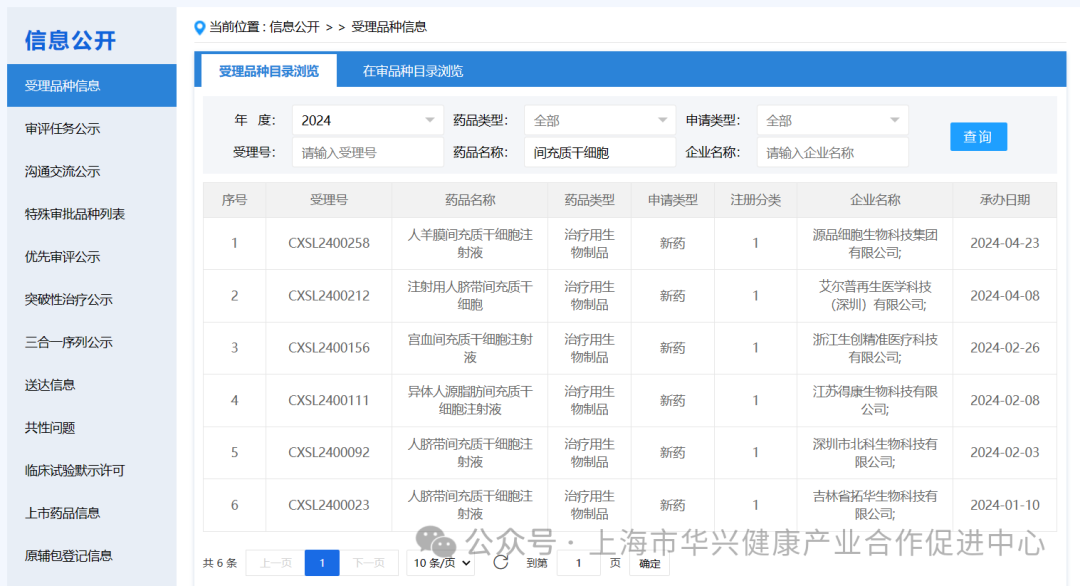
Among them, a total of 6 mesenchymal stem cell drugs were accepted in 2024.
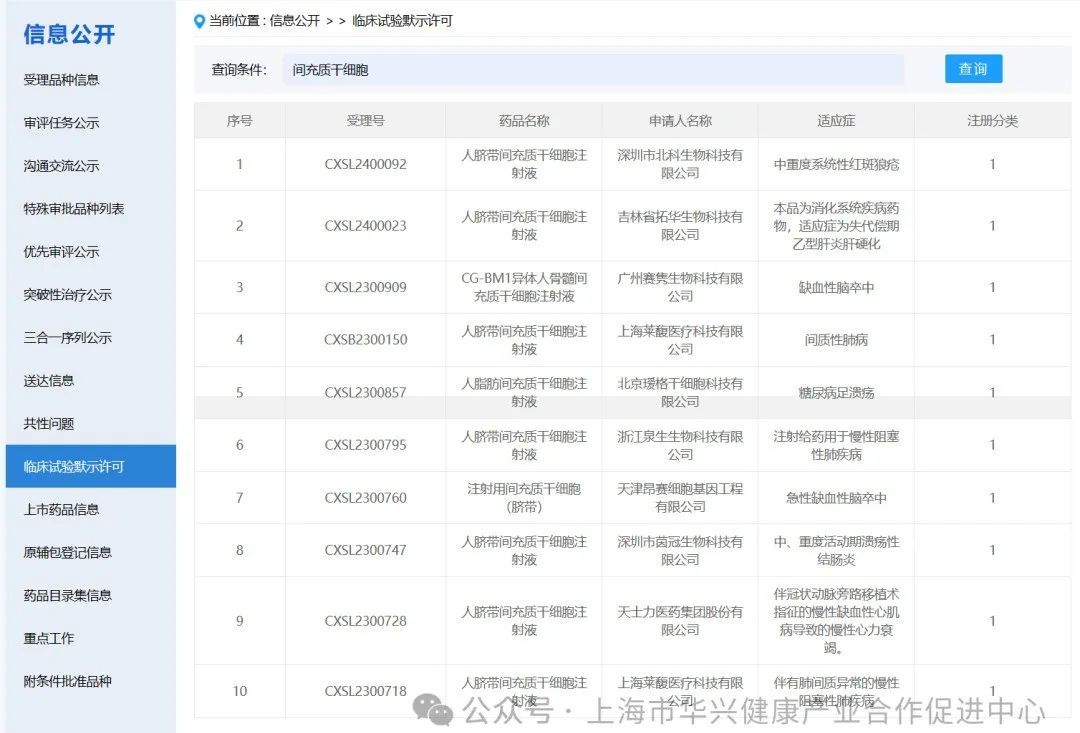
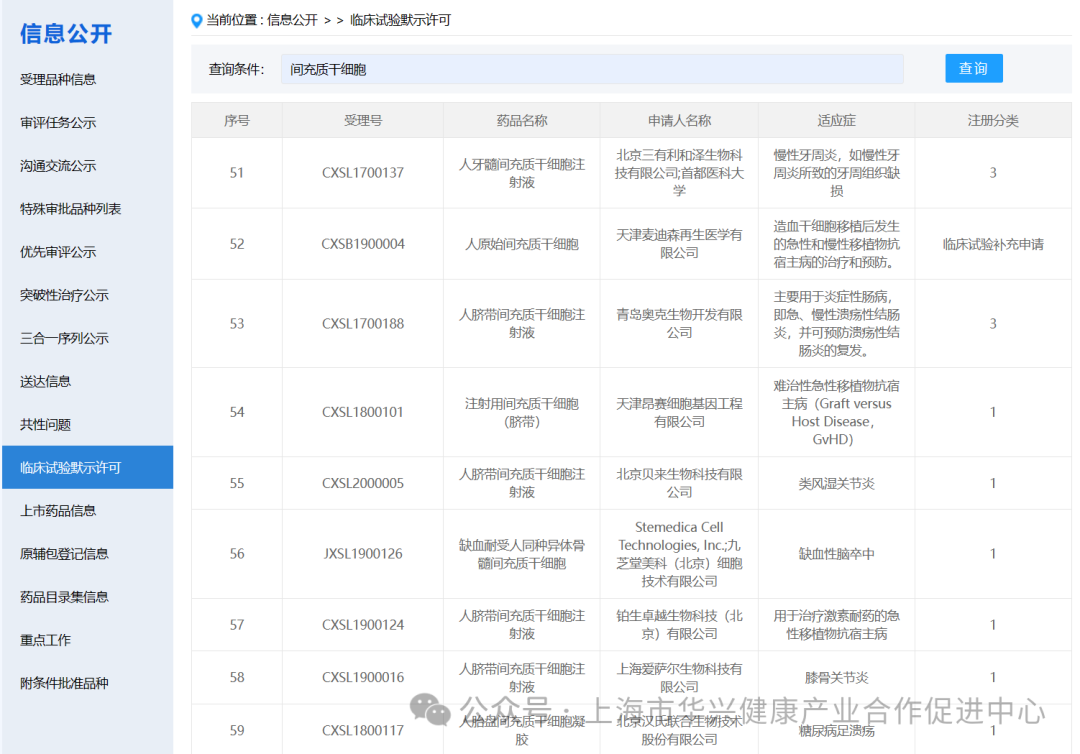
There are 59 mesenchymal stem cell projects implicitly approved by clinical trials in China.
According to the information on the implied permission of clinical trials on the latest CDE official website, as of May 6, 2024, 59 clinical trials with "mesenchymal stem cells" have been implied. (if you add some corporate codes to refer to new stem cell drugs, there are actually more than 60 clinical implied licenses for mesenchymal stem cells in China).
If this year, the first mesenchymal stem cell product remestemcel-L in the United States for steroid refractory acute graft-versus-host disease (SR-aGVHD) children's biological product marketing license application (BLA) can be successfully passed.
There is no doubt that it will give an unprecedented boost to the research and development of new drugs for mesenchymal stem cells in China. Although it has been reported that there are not too many new drugs for stem cells entering the III phase in China, there is only one product of knee arthritis. However, many enterprises have completed the II phase research and are applying to enter the III phase.
In addition, there is a gap in the distribution of stem cell treatment diseases between domestic double filings and IND. In double filings, digestive system diseases (17.7%) are the most, followed by neurological diseases (15.6%) and gynecological diseases (13.5%). In IND, the main indications are respiratory system (26.2%), digestive system (16.9%) and orthopedic diseases (16.9%).
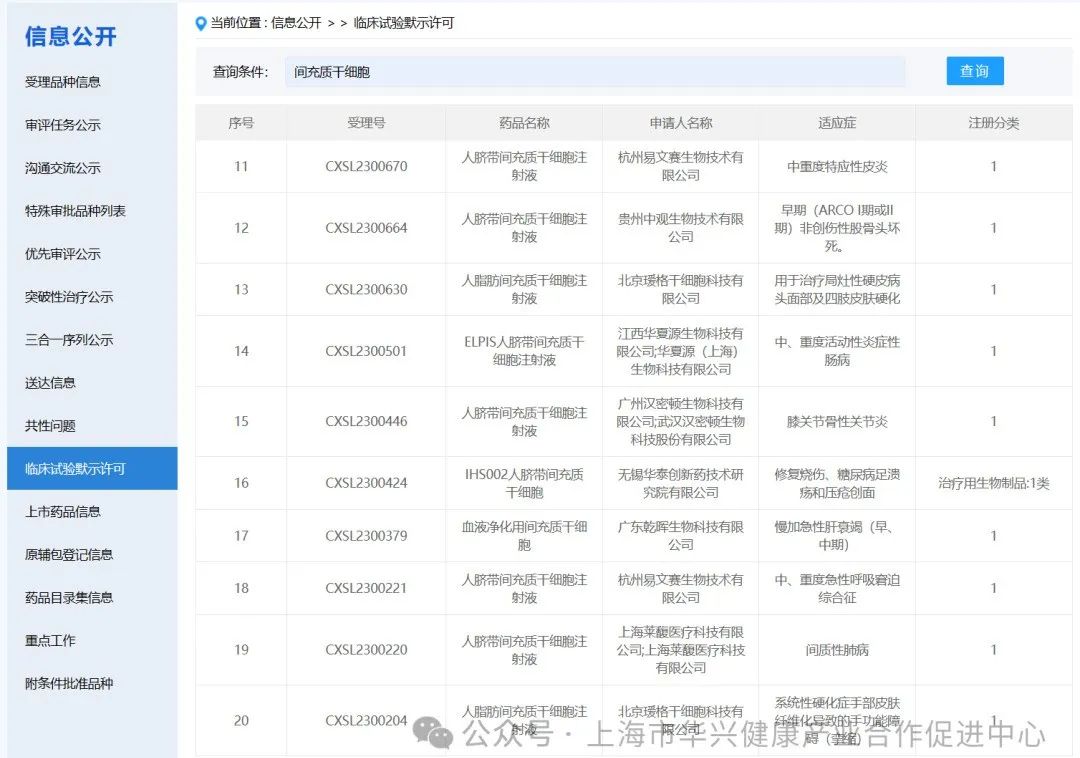
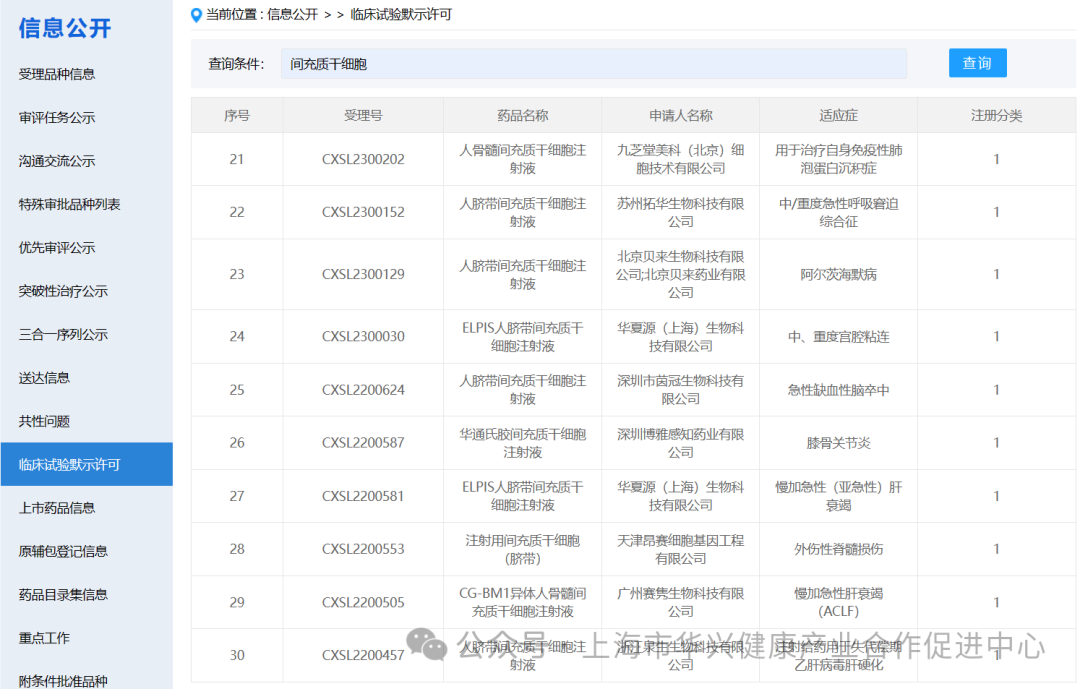
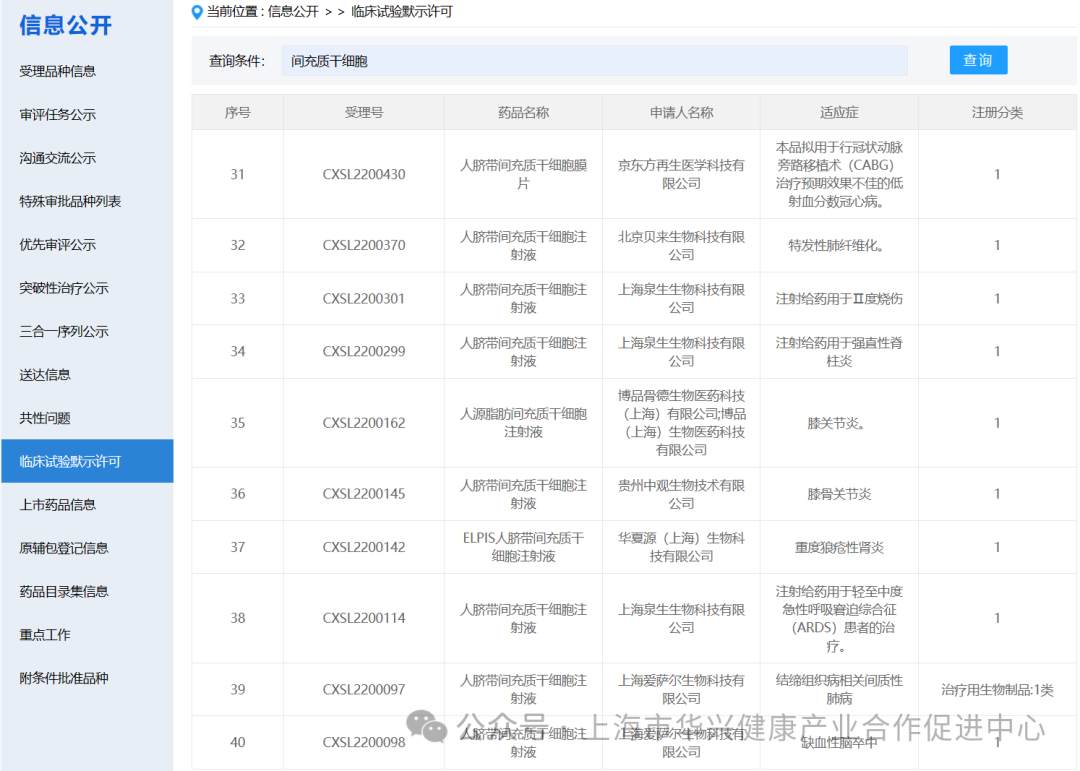
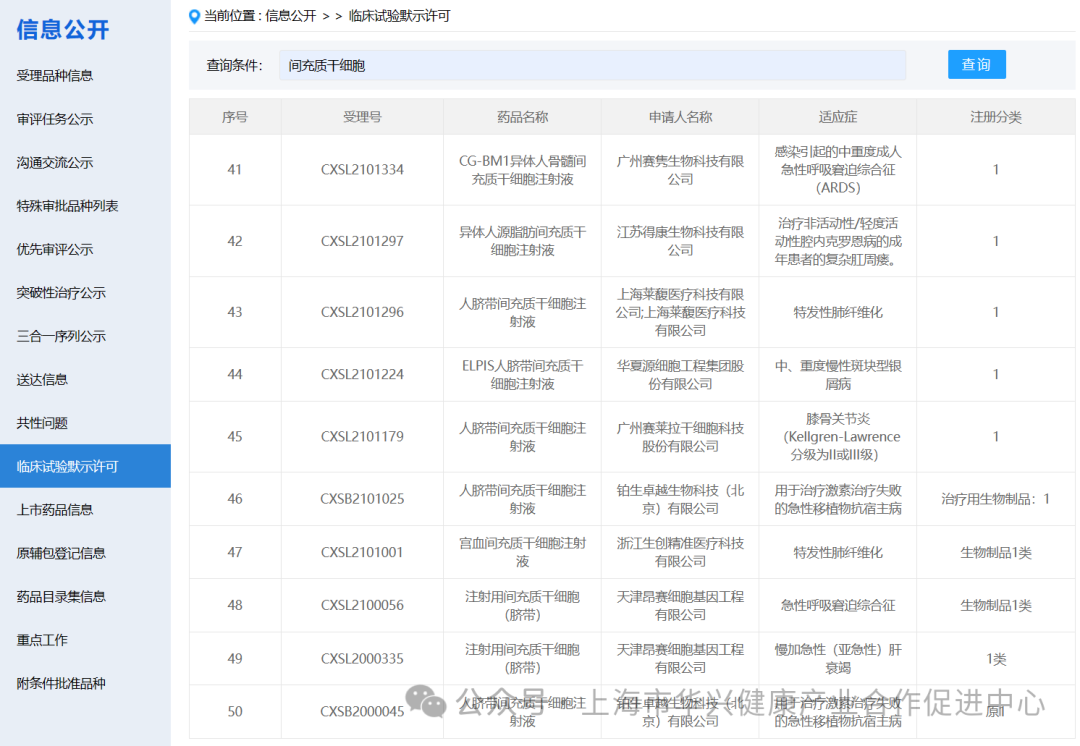
It is worth noting that although mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have shown promising results in preclinical studies, more research is needed to fully understand their potential and develop safe and effective treatments.