
Alzheimer's disease (Alzheimer's Disease,AD) is a group of neurodegenerative diseases that occur in the elderly and presenile. The onset of the disease is hidden and the course of the disease is progressive. With the intensification of China's aging population, the prevalence and mortality of AD in China are increasing, which has become a major public health problem affecting people's health and social sustainable development.
On May 25, at the "2024 Promotion meeting on specialist capacity Building for Cognitive Disorders Diseases" Jointly formulated by the National Neurological Disease Medical Center of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, the Center for Prevention and Control of chronic non-communicable Diseases of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, the capacity Building and continuing Education Center of the National Health Commission, and the China Research Center for population and Development, the Blue Book of Alzheimer's Disease in China (abbreviated as Blue Book) was officially released.
The Blue Book covers the epidemiological characteristics of Alzheimer's disease, economic burden, influencing factors, brain cognitive health index, diagnosis status, treatment status, construction of cognitive impairment diagnosis and treatment centers, community prevention and treatment, patient care, public health resources for prevention and treatment, and so on. Next, let's learn more about it.

Figure 1: blue Book of Alzheimer's Disease in China.
By searching the Chinese and English literatures published from January 2010 to October 2023, the Blue Book systematically analyzed the epidemiological characteristics, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and management of AD and other cognitive disorders in China.
In terms of epidemiological characteristics, the number of AD and related dementia patients worldwide reached 51.62 million in 2019, with China accounting for 25.5%. The prevalence rate is higher than the global average, and AD accounts for 65% of dementia patients. The incidence of AD and related dementia in China is 126.6 / 100000, which increases with age, and it is higher in rural areas than in urban areas.
The risk of AD is related to a variety of factors, including age, sex, education, socio-economic level, genetic factors, lifestyle, disease or dysfunction and environmental factors. Especially with the increase of age, the risk of AD increases significantly, and the risk of AD in women is higher than that in men.
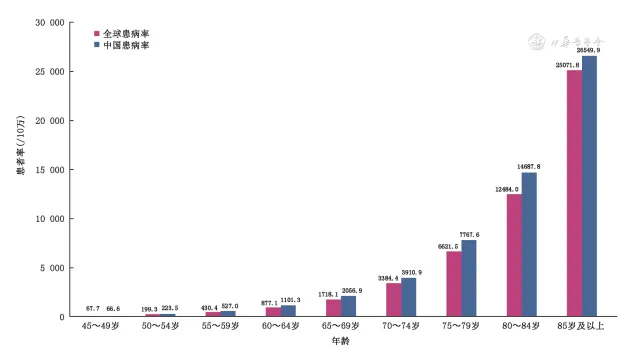 Figure 2. prevalence of AD-related dementia in China from 1990 to 2019
Figure 2. prevalence of AD-related dementia in China from 1990 to 2019
Diagnostic status.
一. Diagnostic differences
At present, there are differences in the diagnosis of AD and other cognitive disorders in different levels of hospitals in China, which affects the accuracy of diagnosis.
In hospitals affiliated to medical colleges and universities, there are usually cognitive impairment diagnosis and treatment centers or memory clinics, equipped with professional medical teams and advanced neuroimaging equipment (such as MRI and PET) and laboratory facilities. Specialists provide standardized diagnostic procedures according to international diagnostic standards and Chinese guidelines; in non-teaching tertiary hospitals in large and medium-sized cities, diagnosis is usually made by neurologists who have not received specialist training in cognitive disorders, and the process is simplified and often depends on personal experience, resulting in some patients may not be able to obtain accurate diagnosis. In the district and county hospitals without cognitive impairment diagnosis and treatment center and memory clinic, it is usually diagnosed by inexperienced physicians, and the proportion of misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis is higher. In addition, advanced auxiliary testing methods, such as biomarker testing and PET testing, are not yet widely available due to high costs and limited resources.
Studies have shown that there is a significant difference in the number of diagnoses between hospitals with and without memory clinics. A survey of a random sample of 36 hospitals showed that before the implementation of the intervention, only 6 hospitals had memory clinics, and the proportion of dementia diagnosis was 0.10%. After the implementation of the intervention, 36 hospitals set up memory clinics, and the proportion of dementia diagnosis increased to 0.41%.
二. Diagnosis delay.
Delayed diagnosis is a prominent problem in AD and other cognitive disorders. The study found that there is a delay from the onset of symptoms to the first visit to a doctor, and patients often have obvious symptoms when they see a doctor. The factors affecting the delay of diagnosis are complex, including patients, family, society and so on. A national survey conducted from 2015 to 2018 showed that of the 2766 patients with dementia and their families, 1974 (71.4%) had never sought medical treatment for dementia, including the belief that "forgetfulness in the elderly is not a disease" (65.1%), "economic hardship" (19.7%) and "sense of shame" (15.2%).
China has formulated a number of AD field guidelines and expert consensus to provide reference for screening, diagnosis and treatment. The whole country is speeding up the construction of the diagnosis and treatment system of cognitive impairment diseases, popularizing the standardized diagnosis path, promoting the application and popularization of advanced auxiliary diagnosis technology, enhancing the popularization of social knowledge, and reducing the phenomenon of stigmatization, so as to achieve the goal of "early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment".
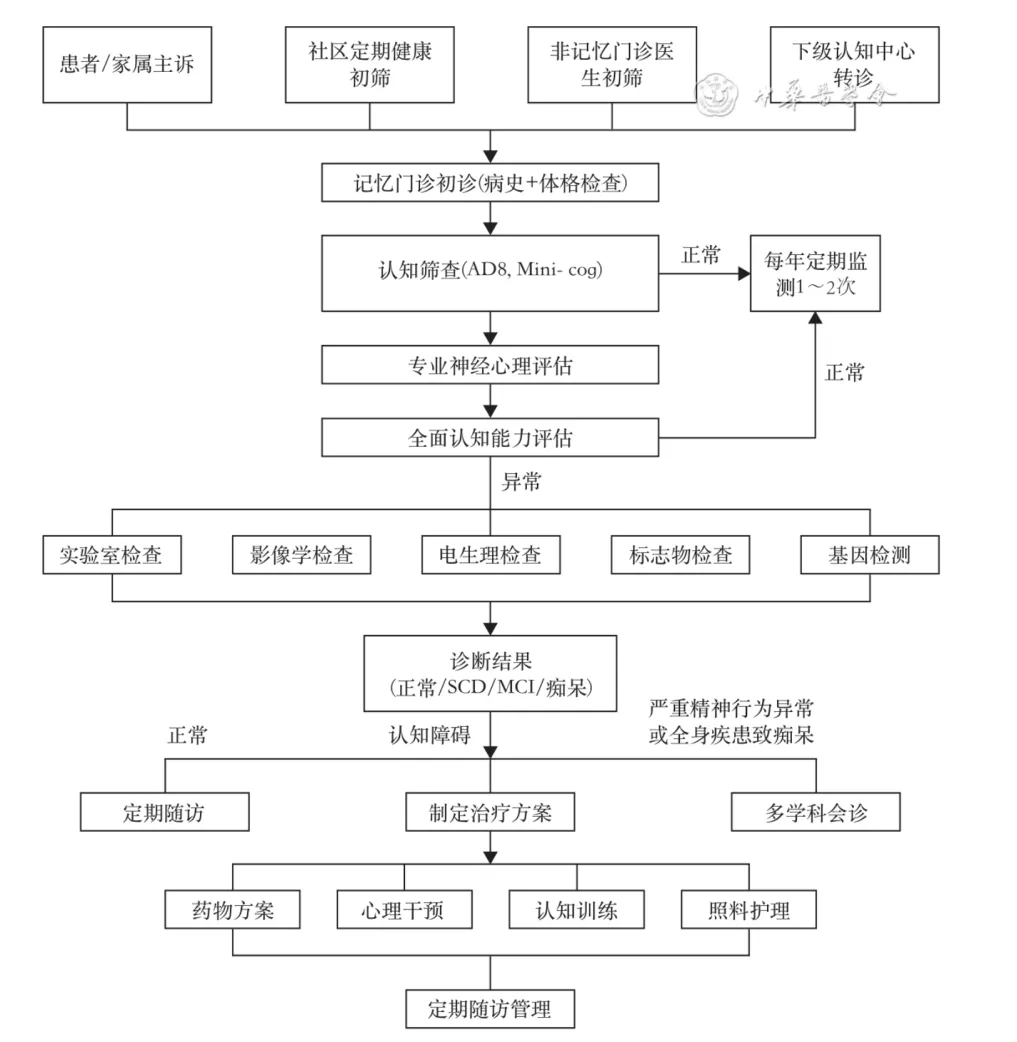 Figure 3: diagnosis and treatment process of cognitive impairment diagnosis and treatment center in China
Figure 3: diagnosis and treatment process of cognitive impairment diagnosis and treatment center in China
Current situation of treatment.
一. Drug treatment
The drugs approved by the State Drug Administration for the treatment of AD include cholinesterase inhibitors (such as Donepezil and carbaratine) and NMDA receptor antagonist memantine. In 2019, Ganlute sodium capsules were approved for the treatment of mild to moderate AD. In January 2024, lenkanab injection was approved for the treatment of mild dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) caused by AD, which can reduce A β plaque deposition and effectively delay the progression of the disease.
Clinically, there are auxiliary drugs such as oxiracetam, Piracetam, brain protein hydrolysate, ginkgo biloba extract tablets, but lack of high-quality evidence-based medicine. Atypical antipsychotics (such as olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (such as citalopram, buspirone) can be used for mental and behavioral symptoms caused by AD. Traditional Chinese medicine has put forward the sequential therapy of "tonifying the kidney in the early stage, resolving phlegm and promoting blood circulation in the middle stage, detoxification and Gutuo in the late stage", which has a synergistic effect combined with western medicine. In recent years, the number of clinical trials of AD drugs in China has increased, and 31 trials have been completed in the past 10 years. Although drug treatment helps to relieve the symptoms of AD, the drug use of patients is still not satisfactory.
二. Non-drug therapy.
Non-drug therapy has made some progress in helping patients maintain cognitive function and activities of daily life and improve mental and behavioral symptoms. It mainly includes cognitive intervention, neuroregulation and exercise therapy.
Cognitive training improves cognitive function and reserve, including orientation, perception, attention, memory, executive function, logical reasoning, processing speed and language function. The Chinese Guide to Cognitive training (2022 Edition) and the Chinese expert consensus on Cognitive Digital Therapy (2023) issued in 2019 further provide a basis for clinical treatment. There is no obvious adverse reaction in cognitive training, and the scheme and content should be optimized according to the latest progress in the future.
Neuroregulation regulates the signal transmission of the nervous system in physical or chemical ways to improve disease symptoms. It mainly includes brain functional stimulation (invasive and non-invasive), such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation, transcranial AC electrical stimulation and photobiological regulation. These techniques are non-invasive and have few adverse reactions, and related clinical trials have shown effects, which are helpful to maintain or improve the cognitive function, quality of life and activities of daily life of AD patients. The consensus of Chinese experts on the treatment of Alzheimer's disease assisted by non-invasive neuroregulatory techniques released in 2023 provides clinical recommendations for the selection of appropriate treatments.
Summary and prospect.
The Blue Book of Alzheimer's Disease in China 2024 comprehensively analyzes the epidemiological characteristics, diagnosis and treatment of AD in China, and reveals the significant differences in diagnosis and treatment among different levels of hospitals. The affiliated hospitals of medical colleges and universities have advantages in professional diagnosis and treatment, while grass-roots hospitals are faced with the shortage of equipment and professionals, resulting in a high rate of misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis. Drug and non-drug therapy have made some progress in improving the quality of life of patients, but the use of drugs is still not satisfactory. Family care is the main form of care, and the long-term care insurance system is being gradually promoted.
In the future, it is necessary to strengthen the training of medical staff, improve the ability of diagnosis and treatment, promote early screening and intervention, optimize prevention and treatment policies, improve the social support system, and reduce the economic burden of patients and their families. Through the continuous improvement of the diagnosis and treatment system and policy support, efforts should be made to achieve early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment of Alzheimer's disease, improve the quality of life of patients and promote the healthy and sustainable development of society.