
In the human body, there is a special type of cells that have the ability to self-renew and can differentiate into multiple tissue cell types. They are called "stem cells." Because of its special capabilities, regenerative medicine, represented by stem cells, has become a research object of much attention in the medical field in recent years, bringing potential hope and choices to human health.
However, there are many types of stem cells, and there are also two derivatives of "exosomes" and "supernatant". There are considerable differences between different types.
Classification by development stage: embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells...
01. Embryonic stem cells (ES cells)
ES cells are totipotent stem cells isolated from early embryos or inner cell masses. They can be differentiated into almost all types of human cells. They have strong self-renewal capabilities and extensive differentiation capabilities, and can be used for the protection and repair of organ or tissue damage.
ES cells have broad application potential in the treatment of diabetes, bone and cartilage diseases, liver diseases, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, trauma or burns, but there are certain ethical limitations.
▼Common types of stem cells
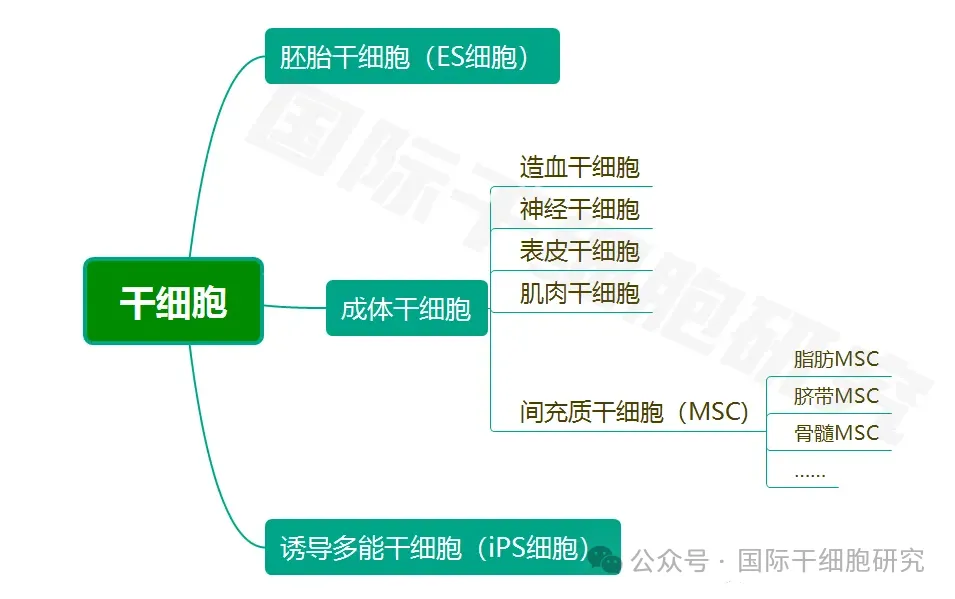
02. Adult stem cells
It is a type of primitive cell with proliferation ability, self-renewal and multi-directional differentiation potential. It exists in specific differentiated tissues and organs. Its main role is to promote tissue repair and regeneration. It has no ethical issues and is a type of stem cell with a wide range of applications. Common types include mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), neural stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, epidermal stem cells, muscle stem cells and other types.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are a type of adult stem cells with self-renewal, tissue regeneration, immunoregulation capabilities, and multi-lineage differentiation potential. They also have the advantages of being easy to obtain and isolate, and have become an ideal source for different clinical applications. Depending on their sources, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be subdivided into many types such as fat MSC, umbilical cord MSC, bone marrow MSC, dental pulp MSC, etc.
Mesenchymal stem cells are used to prevent and treat various chronic diseases (such as bone and joint diseases, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, nervous system diseases, liver and kidney diseases or cardiovascular diseases, etc.), improve immunity, and beauty and anti-aging.
▼Clinical use of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine and cell therapy (by disease category)
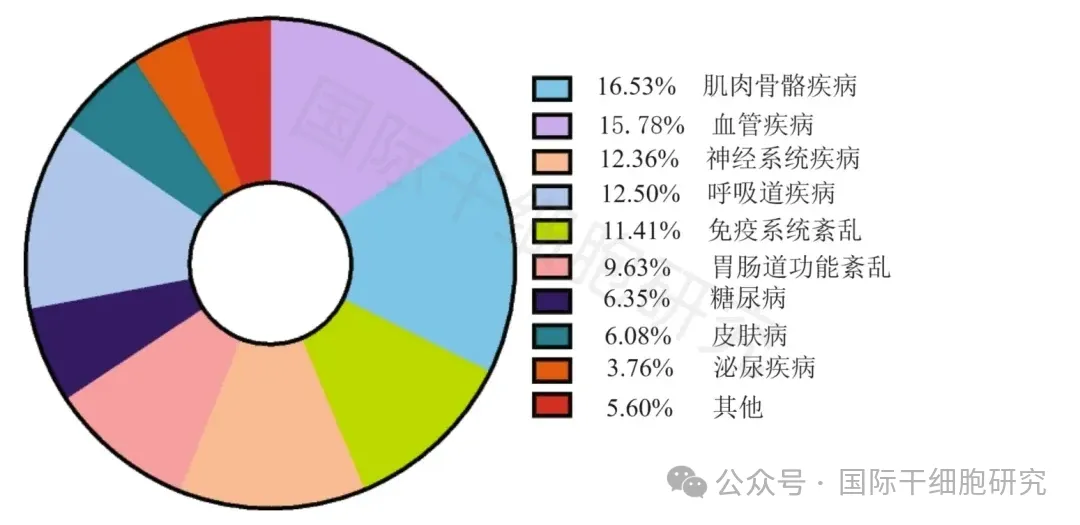
▲图源“BMC”
03. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells)
iPS cells, also known as "reprogrammed stem cells", are a type of pluripotent stem cells obtained by reprogramming mature cells. It has the multi-directional differentiation potential and high proliferation activity similar to embryonic stem cells, and there are no ethical issues. It is reported that Japan has always been in a leading position in the research and development of induced pluripotent stem cells, and Professor Nobu Yamanaka won the 2012 Nobel Prize for this research.
However, iPS cells have certain genetic instability, and most of them are currently in clinical research. However, it is gratifying to note that the Center for iPS Cell Research and Applications (CiRA) of Kyoto University in Japan has cooperated with Astellas Pharmaceuticals to launch the second phase of research on iPS cells, aiming to target refractory diseases that traditional methods are unable to do anything. Let's wait and see!
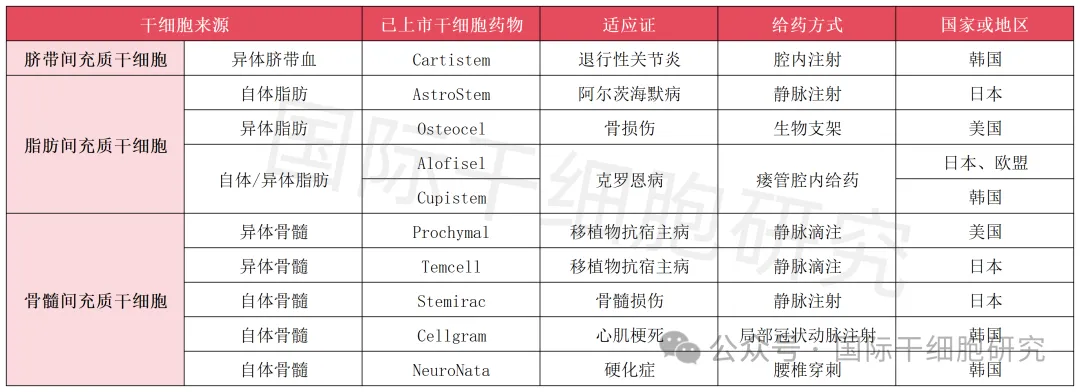
Table 1 Summary of approved stem cell products
Classification by donor source: autologous stem cells, allogeneic stem cells
01. Autologous stem cells
Stem cells are obtained from the patient's own tissues (such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, peripheral blood, etc.). Because stem cells originate from the patient itself, they are integrated faster in the production of immune system cells and new blood, and the risk of rejection is extremely low.
Japan, as one of the few countries that has approved the use of stem cells, divides autologous stem cells into the second category of regenerative medicine. Currently, it has been approved for clinical use. Common types include autologous adipose mesenchymal stem cells, autologous synovial stem cells, autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, autologous menstrual blood stem cells, MSC derived from autologous endometrial tissue, and many other types.
However, autologous stem cells also have certain limitations, such as certain trauma and pain during the extraction process, and the treatment process is relatively long. For example, one reinfusion of autologous stem cells requires at least two treatments, one time to extract stem cells and the other time to reinfusion stem cells.
02. Allogeneic stem cells
Stem cells extracted from tissue (such as donated pulp, cord blood, cord cord, etc.) donated by donors (such as family members or strangers).
Allogeneic stem cells do not need to be extracted from the patient themselves, so they are less traumatic and painful, and the treatment process is relatively simple. Allogeneic stem cells are currently used in clinical research in my country (such as allogeneic cord mesenchymal stem cells, allogeneic pulp mesenchymal stem cells, etc.).
However, allogeneic stem cells have certain limitations. They are not as stable as autologous stem cells. They may also have a certain degree of immune rejection. However, under normal circumstances, immune rejection is not obvious.
In summary, patients can make reasonable choices based on their own circumstances and needs.
Stem cell derivatives: stem cell exosomes, stem cell supernatant
Stem cells are treasures. In addition to the cells themselves, the stem cell exosomes and stem cell supernatants derived from them have gradually become research hotspots in recent years, and they have become popular for a time!
01. Stem cell supernatant
It is the upper high-purity clarified culture medium obtained during the stem cell culture process. It contains exosomes, growth factors, etc. It can be extracted and cultured from various stem cells such as umbilical cord, adipose tissue, bone marrow, and placenta, and is generally stored at room temperature.
Stem cell supernatant contains a large number of cellular active factors (such as exosomes, growth factors, etc.), which can improve cell survival, activate cell activity, and accelerate tissue repair. Although it cannot completely fill the gap in stem cells, it can exert similar effects to stem cells.
02. Stem cell exosomes
Stem cell exosomes are nanoscale vesicles secreted by stem cells. They carry a variety of genetic information and functional proteins, such as nucleic acids, lipids, proteins, etc., and can be derived from mesenchymal stem cells, pluripotent stem cells, etc. In almost all types of cells. It needs to be stored at about-20℃ and can only be frozen for about 6 months. Too long time or too high temperature may lead to a decrease or loss of exosome activity.
Exosomes are equivalent to "freight trucks" and are important pathways for inter-cell communication. They can smoothly pass through human tissue barriers, open cell signaling channels, and ultimately affect the function of recipient cells.
If stem cells are compared to "fish kept in a fish tank", then the stem cell supernatant is equivalent to "the remaining water in the fish tank after removing the fish"; the exosecretion is equivalent to "the purified water obtained by filtering and purifying the remaining water in the fish tank." Obviously, compared with the supernatant, exosomes have higher purity and purification requirements, and have fewer side effects, which is expected to become an "alternative to stem cells."

Summary
American biologist George Daly once said,"If the 20th century is the era of drug treatment, then the 21st century is the era of cell therapy!" The emergence of stem cells and their derivatives has brought new hope and choices to areas where traditional medicine is helpless, such as chronic disease prevention and treatment, beauty and anti-aging, and cancer treatment (hematopoietic stem cells)!
Although there are many members of the stem cell family, their characteristics and division of labor are different. By exploring the characteristics and applications of stem cells, we can reveal the wonderful journey of body regeneration and make important contributions to treating diseases and promoting human health! During clinical application, doctors will comprehensively consider the patient's individual condition, disease type, stem cell characteristics and research status, domestic policies and other factors before selecting the appropriate type.