
Source: BioValley
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, and irreversible lung disease characterized by pulmonary fibrosis and impaired lung function, eventually leading to respiratory failure. Many studies have found that stem cell exosomes have great potential in the intervention of fibrosis. Among them, mesenchymal stem cell exosomes (MSC-Exos) are the most widely studied. They contain rich bioactive substances, which can reduce inflammation, inhibit the formation of fibrous scar tissue, and promote the regeneration of damaged tissue. Our previous studies showed that human embryonic stem cell exosomes (hESC-Exos) were superior to MSC-Exos in regulating damage repair through omics analysis. However, the intervention effect of hESC-Exos in pulmonary fibrosis has not been reported.
On September 4, 2023, The journal Stem Cell Research &Therapy published online the title "Exosomal miR-17-5p prevents human embryonic stem cells from the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Ji Guangju pulmonary fibrosis by targeting thrombospondin-2". This study is the first to report the significant effects of hESC-Exos in the treatment and prevention of pulmonary fibrosis and elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved, providing a new perspective for drug development in fibrosis-related diseases. The results showed that hESC-Exos injection significantly reduced inflammation, cleared collagen deposits, repaired damaged alveolar structures, increased lung blood flow, and improved lung function in mice.
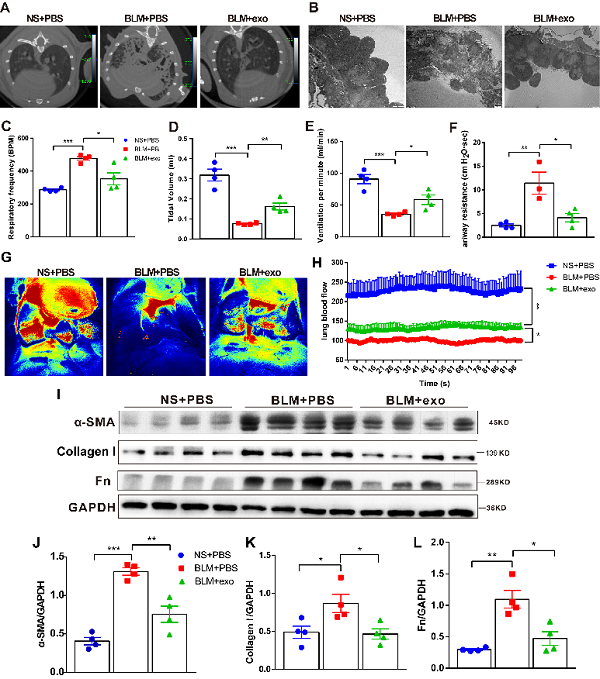
Figure 1 hESC-Exos remodeled fibrotic lung structure and improved lung function
In terms of mechanism, studies have found that hESC-Exos carries a high abundance of miR-17-5p to regulate the expression of fibrosis-related gene Thrombospondin-2 (Thbs2), thereby interfering with the progression of pulmonary fibrosis.
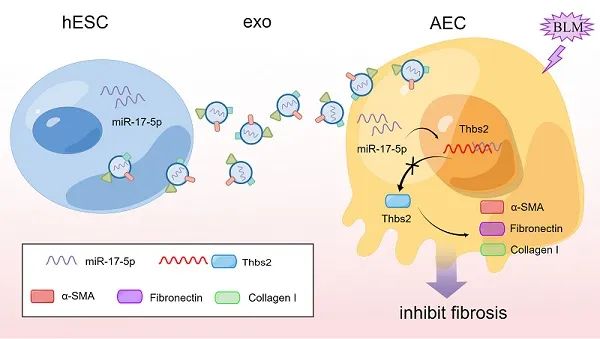
Figure 2 hESC-exo alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by reducing Thbs2 expression by delivering miR-17-5p to BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis
This study is the first to report the intervention effect of hESC-Exos in pulmonary fibrosis, which shows good immune regulation and damage repair ability. This study further suggests that hESC-Exos has a good application prospect in fibrotic diseases.
Researcher Ji Guangju and Associate Researcher Wang Huiwen from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences are the corresponding authors of the paper, and doctoral students Liu Qun and Bi Youkun from the Ji Guangju group are co-first authors. This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The original link: ttps://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-023-03449-7