
The research team of the School of Biomedicine of the University of Hong Kong Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine (hereinafter referred to as "HKU School of Medicine") has recently made a breakthrough in stem cell research. The team has developed an innovative way to transform blood and skin cells into neural stem cells. The emergence of this research results, on the one hand, overcomes the limitations of the current stem cell research technology; on the other hand, it provides a new choice and hope for the treatment of age-related diseases (such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc.). The relevant research results are simultaneously published in the world-famous journal Scientific Progress (Science Advances).
Faculty of Medicine, HKU: exploring shortcuts in the research and development of neural stem cells to treat age-related diseases

The human body is made up of more than 200 different types of cells, each of which plays a key role in maintaining overall health. However, it has been difficult to obtain and analyze certain special types of cells, such as neurons in the depths of the brain. In addition, traditional induced pluripotent stem cells (IPS) and embryonic stem cells usually can not fully capture the characteristics of aging cells, which limits their application in the treatment of age-related diseases.
To address these limitations, the HKU Faculty of Medicine team achieved rapid and effective cell transformation by transforming a powerful molecule called "SOX17" into a "super stem cell factor" that organizes itself in the nucleus and precisely navigates from one gene to another. At present, the team has submitted a non-temporary patent application for the use of engineered SOX17 to develop a next-generation stem cell model and retain aging stem cells, providing more valuable data for the study of potential treatments for age-related diseases. The next phase will focus on nerve cells produced in the blood cells of the elderly.
These studies mark an important milestone in the field of stem cell research. We can use stem cells to treat a variety of aging-related diseases and unlock personalized treatment strategies to meet the unique needs of individual patients! " Professor Ralf Jauch, Associate Professor, School of Medicine, HKU and Chief researcher, Centre for Transforming Stem Cell Biology
Aging popular science
Aging refers to the gradual degradation of the body with age, characterized by the accumulation of aging cells and inflammatory factors, leading to the occurrence of a variety of aging-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, osteoporosis, premature ovarian failure (POF), cardiovascular disease (CVD) and so on.
Aging is usually accompanied by cell aging, which is the key mechanism of aging. In addition, endogenous stem cell depletion may also be involved in the aging process. Compared with young mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), aging mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) show a decrease in cell activity, immunomodulatory ability and secretion of factors (such as anti-inflammatory factors, growth factors, etc.).
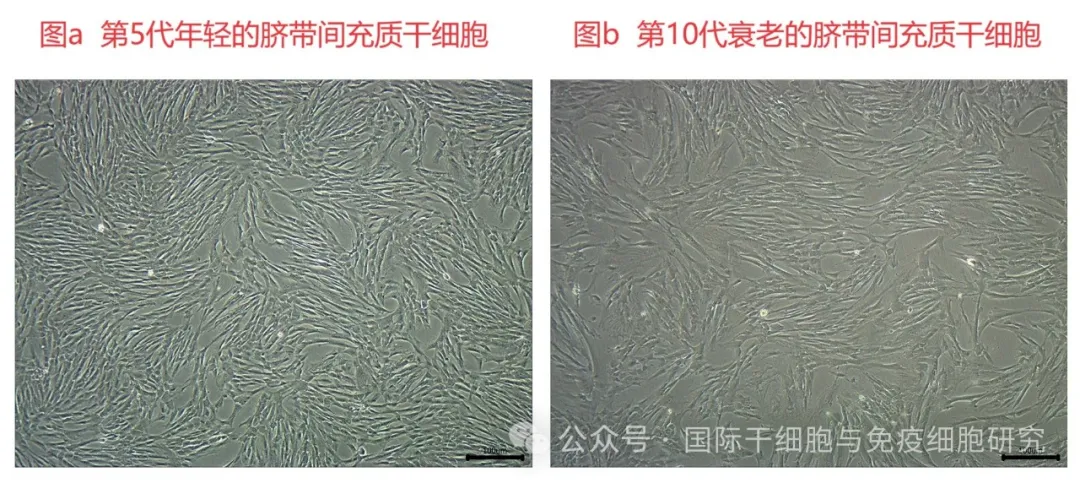
In addition, the morphology of senescent cells will also change, for example, with the aging of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs), the morphology of cells can change from slender fusiform to large and flat shape (see figure below).
How to delay aging?
At present, studies have found that cell therapy, represented by mesenchymal stem cells, is a potential treatment for delaying and fighting aging-related diseases. In addition, appropriate nutritional intervention, strengthening exercise, calorie restriction and maintaining iron homeostasis also help to delay the aging process to a certain extent.
Cell therapy against skin aging.
As the barrier of the body, the skin will have aging or pathological changes with aging, and the skin state is also one of the intuitive manifestations of aging, which may be caused by the accumulation of senescent cells, the loss of collagen, the increase of matrix metalloproteinases and oxidation activity.
Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are pluripotent cells, which can produce mesenchymal and non-mesenchymal tissue in vivo and in vitro, and have the ability of self-renewal and multi-directional differentiation. MSC can secrete factors needed for skin regeneration, inhibit the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and increase the synthesis of collagen, so it has a good application prospect in skin regeneration.
Mesenchymal stem cells can promote skin regeneration by increasing cell proliferation and new angiogenesis. In addition, it can also prevent the aging problem caused by ultraviolet rays through tissue structure regeneration and the production of collagen and elastin fibers.
Cell therapy against hair problems caused by aging.
Hair loss and gray hair is also one of the direct manifestations of aging. Among them, hair loss is related to hair follicle degeneration, although it can be treated by surgery (such as hair transplant) or drugs (such as minoxidil), but its curative effect is limited, it is not suitable for all patients, and there are certain side effects.
Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have the ability of migration, homing and differentiation, as well as paracrine, and can release a variety of nutritional factors (such as cytokines, growth factors, etc.). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) play an important role in hair regeneration and repair.
1. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC): it can promote the proliferation of hair follicle stem cells (HFSC) and transform hair follicles from quiescent phase to growing stage, thus promoting hair follicle regeneration and hair growth.
2. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSC) have the ability to protect dermal papilla cells of hair follicles and treat alopecia.
3. Other stem cell cells, such as hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells, dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells, adipose mesenchymal stem cells, amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells and so on, can also accelerate hair regeneration and have a certain therapeutic effect on hair loss.
Cell therapy against immune senescence
Aging can lead to aging of the immune system, destroy the homeostasis of macrophages, and increase the morbidity and mortality of the elderly. this phenomenon is called immune aging. With the rapid increase of life expectancy of the elderly, the immune system has gradually become the main driver of age-related diseases. The aging of immune system is a dynamic and gradual process. Studies have shown that after the age of 30, the activity of the thymus decreases at a rate of 2% to 3% a year, resulting in a significant decrease in the activity of individuals aged 50 to 65, although the aging thymus will continue to play an immune function, but the production of T cells is significantly reduced, and the effect may also be greatly reduced. For example, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis and so on, are common diseases related to aging.
Therefore, how to rebuild or enhance the immunity of the body is one of the important means to combat aging-related diseases. In recent years, it has been found that cell therapy helps to counteract immune aging and age-related immune dysfunction. Interventional immune regeneration strategies mainly have two ideas: one is to focus on regenerating aging immune organs to restart the patient's immune system; second, to directly rebuild the immune system through artificial replenishment of cells, microenvironment or tissue. The following is an example of stem cells and NK cells commonly used in clinic to briefly introduce how to improve the body's immunity through cell therapy.
1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC).
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have unique immunomodulatory ability to participate in tissue regeneration and maintain balance in vivo.
On the one hand, it can directly affect congenital and adaptive immune cells (such as NK cells, DC cells, macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes) to restore immune homeostasis.
On the other hand, mesenchymal stem cells are known regulators of thymic degeneration, which can regulate the structure and activity of thymus and prevent, slow down or reverse the process of thymic degeneration.
2. NK cells.
Natural killer cells (natural killer,NK) are the core cells of innate immunity, patrolling the blood vessels of the whole body all the time, exercising the function of immune surveillance, discovering and eliminating "alien" such as cancer cells, infected cells and aging cells at the first time, so it is also known as the first line of defense of the body against cancer and infection, and plays a key role in clearing tumors and fighting infection.
NK cells can also be used as key regulators of adaptive immunity, because they can regulate adaptive immunity by targeting dendritic cells, and activate and recruit components of innate and adaptive immune responses by releasing chemokines, inflammatory cytokines, cytolytic particles and so on.
Cell therapy improves premature ovarian failure (POF).
Premature ovarian failure (POF) is a common endocrine disease, which can lead to female infertility. Its pathogenesis may be related to autoimmunity, genetic defects, chemotherapy damage, age and other factors. With the increase of age, most of the follicles are depleted and the ovarian function is impaired, which can eventually lead to premature ovarian failure. At present, hormone therapy is mainly used, but this method can not restore ovarian function.
The emergence of stem cell therapy brings new hope for patients with premature ovarian failure. Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells have immunomodulatory effect, which can increase the release of anti-inflammatory factors and inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory factors, thus helping to promote follicular survival and improve premature ovarian failure.
In a study on "umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSC) for the treatment of premature ovarian failure", patients were divided into two groups: stem cell treatment group (receiving UC-MSC transplantation) and combined treatment group (receiving UC-MSC combined with collagen transplantation). After an one-year follow-up, the results show that mesenchymal stem cells have a good effect in the treatment of premature ovarian failure. Among them, UC-MSC improved the activation and growth of follicles, while UC-MSC combined with collagen transplantation contributed to the long-term recovery of ovarian function and improved the fertility of patients to some extent.
Cell therapy improves neurodegenerative diseases.
With the progress of aging, the incidence of some neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, etc.) also increases. Aging is one of the main risk factors of neurodegenerative diseases.
Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have the ability of migration and homing and play a role in the aging brain; in addition, neural stem cells (NSC) can produce new neurons and help to improve the function of the central nervous system.
Cell therapy improves osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a progressive systemic bone disease related to age, which is characterized by low bone mass and high bone brittleness. In patients with osteoporosis, the ability of MSC to differentiate into osteoblasts is decreased, but the ability to differentiate into adipocytes is enhanced, which eventually leads to a decrease in bone formation. Although some drugs are helpful in the treatment of the disease, they are not effective for all patients and may cause adverse reactions. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new treatments.
Recent studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can not only secrete factors involved in bone repair, but also have the ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes and adipocytes. Therefore, MSC can be used as an alternative therapy for age-related osteoporosis and has a wide application prospect in the treatment of osteoporosis.
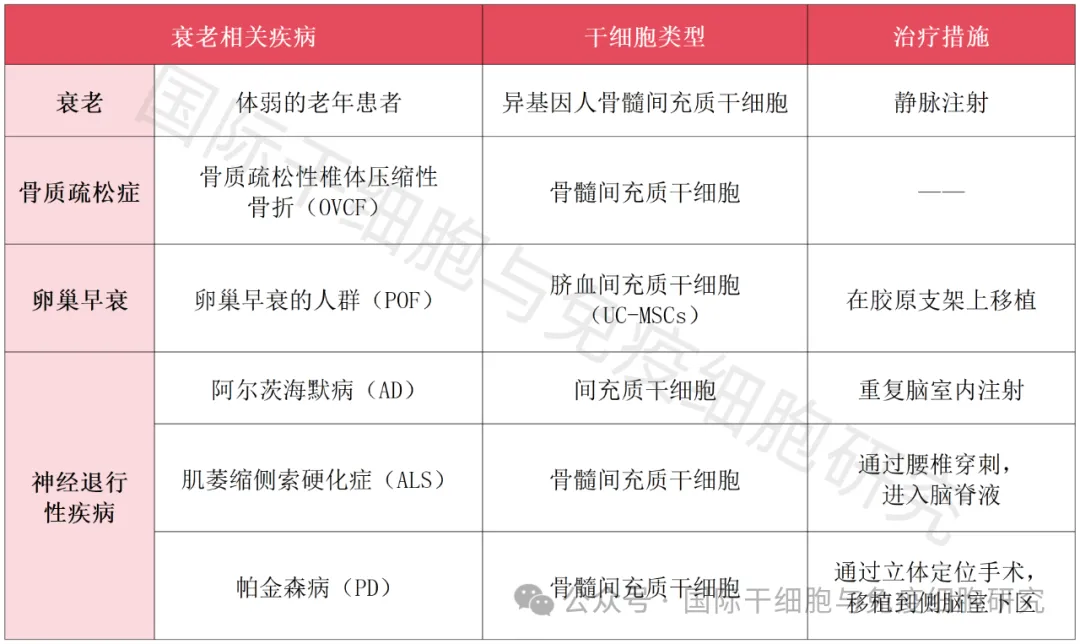
▼Clinical study of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of aging-related diseases
Collection of International Stem Cell and immune Cell Research Medical Department
Summary.
Aging not only affects our appearance, but also may cause a variety of age-related diseases, such as hair loss, neurodegenerative diseases, osteoporosis, premature ovarian failure and so on. Therefore, it is of great significance to deeply understand the causes of aging and explore more effective measures to delay or even reverse aging.
Recent studies have found that with the development of regenerative medicine, cell therapy represented by stem cells has a broad application prospect in the field of anti-aging, which is helpful to delay aging, combat aging-related diseases and enhance immunity. It is gratifying that there are some clinical trials based on stem cells in the treatment of aging and aging-related diseases, which have preliminarily proved the effectiveness and safety of cell therapy.
Reference:
[1]Wang Y,et al.Application of mesenchymal stem cells for anti-senescence and clinical challenges. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Sep 19;14(1):260.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10510299/
[2]Weng M,et al.An engineered Sox17 induces somatic to neural stem cell fate transitions independently from pluripotency reprogramming[J].Science advances,2023,9(34):eadh2501.
https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/sciadv.adh2501?rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-