
Recently, the University of Hong Kong School of Medicine collaborated with a research team at the University of Cambridge to create a new stem cell model that provides a personalized new treatment option for patients with rare immunodeficiency diseases that were once often considered untreatable or an incurable "orphan disease."
The researchers first took blood samples from patients and then reengineered the patients 'cells into expanded potential stem cells (EPSC). After initially achieving significant success in treating rheumatism, the research team re-explored its potential in treating other immune system diseases and brought great hope to patients, the results were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.

▲ The screenshot comes from the "University of Hong Kong official website"
What is an autoimmune disease?
Autoimmune diseases (AID) mostly occur due to dysfunction of the immune system that mistakenly attacks one's own cells and tissues. About 8% to 10% of patients are affected by autoimmune diseases, which is the world's third largest burden after cancer and heart disease.
There are more than 80 common autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes (caused by the immune system destroying pancreatic beta cells), rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease, Sjogren's syndrome, autoimmune liver disease, etc.
Stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types and play a key role in immune regulation and regenerative therapy. In addition, due to the limitations of traditional treatment methods, researchers have been trying to use stem cell therapy in recent years as an alternative source for treating autoimmune diseases.
What are the common autoimmune diseases?
01. Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1DM) is a group of autoimmune diseases in which autoreactive immune cells, especially CD4 + T cells, target pancreatic beta cells, resulting in complete insulin deficiency. About 90% of T1DM is caused by stimulation of autoantibodies against the insulin-producing pancreatic islets, and only 10% to 20% of patients remain functional due to defects in the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells.
02. Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease characterized by synovial hyperplasia, joint inflammation, progressive joint damage, and cartilage and bone destruction, and symptoms may gradually worsen over time. Patients also have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis is related to an imbalance in immune homeostasis, especially between Th17 (T helper cells 17) and Treg, which causes autoreactive immune cells to be activated and attack collagen-rich joint areas. Currently, common treatment methods, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, slow-acting anti-rheumatic drugs, etc., may cause side effects such as gastrointestinal damage, liver and kidney damage, etc. When taken for a long time, there is an urgent need to find new treatment methods.
03. Systemic lupus erythematosus
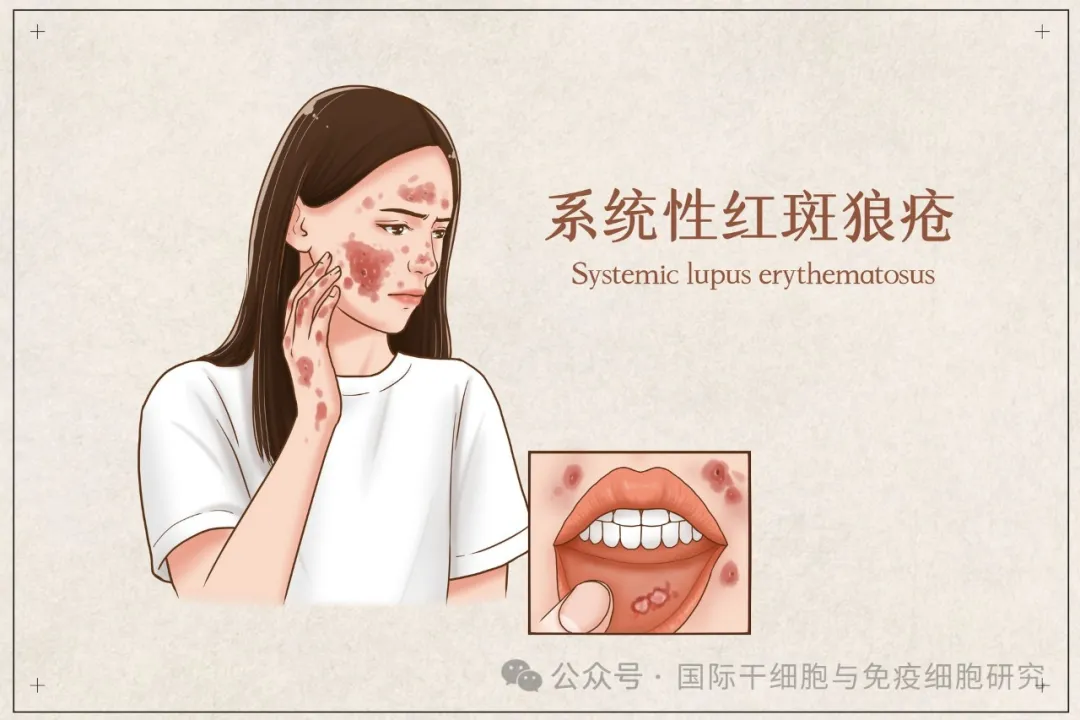
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by the large production of nuclear autoantibodies, resulting in the deposition of antibody-antigen immune complexes in various organs. It may be related to Bggs (regulatory B cells), Th1/Th17/Tggs imbalance, etc.
04. Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that may be associated with demyelination and progressive neurodegeneration of the central nervous system. Existing treatment methods (such as medication, etc.) cannot reverse the continuous progression of multiple sclerosis.
05. Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal and autoimmune disease that is mainly caused by genetically susceptible hosts that produce inappropriate and sustained immune responses to pathogens. Common include Crohn's disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC).
06. Autoimmune liver disease
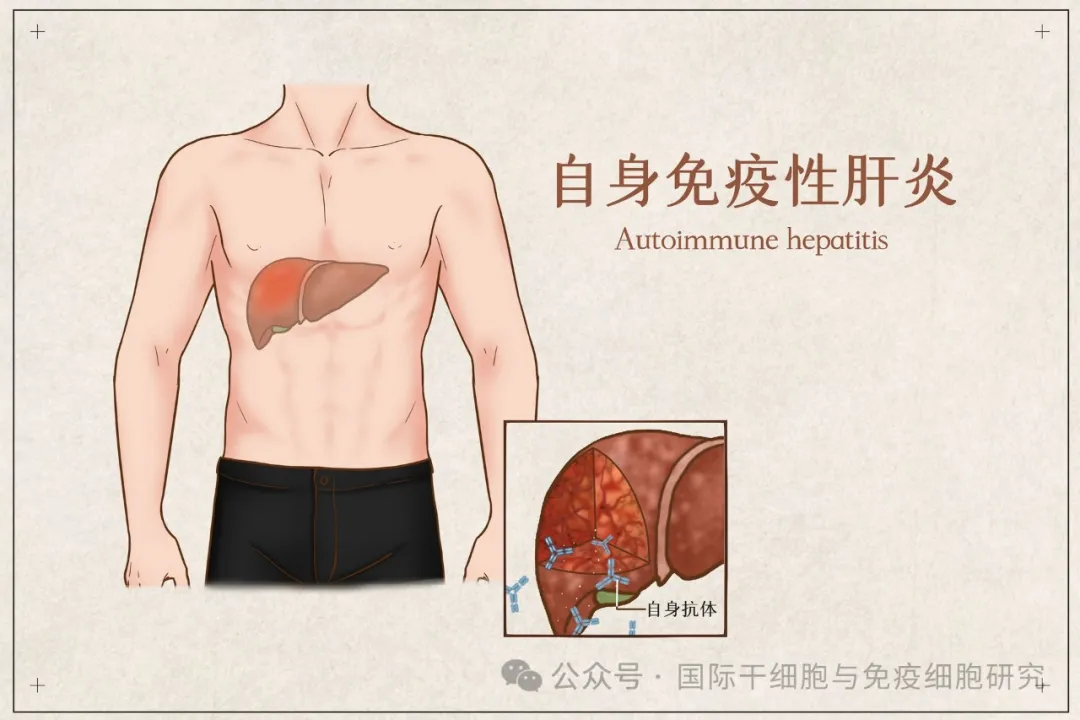
Autoimmune liver disease (AILD) is one of the chronic kidney diseases caused by immune system dysfunction. It commonly includes autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and primary biliary cholangitis (PBC).
Patients can see liver pain, loss of appetite, fatigue, scleral jaundice (yellow eyes) and other manifestations; laboratory examinations will reveal abnormal levels of liver function markers and the presence of autoantibodies in blood tests.
07. Sjogren's syndrome
Sjogren's syndrome (SS) is one of the three most common autoimmune diseases. Lymphocytes penetrate into the lacrimal and salivary glands. It is characterized by dry eyes, dry mouth, and joint pain.
Stem cell therapy: new hope for autoimmune diseases!
01. Stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes
A clinical study on the use of stem cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetes was conducted. A total of 42 patients were enrolled. After enrollment, they were randomly treated with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSC) and autologous bone marrow monocytes (BM-MNC).
The results showed that within 1 year of treatment, the enrolled patients had decreased fasting blood glucose, decreased glycosylated hemoglobin, increased C-peptide, and reduced daily insulin demand. The above studies show that UC-MSC and BM-MNC can help improve metabolic indicators in patients with type 1 diabetes.
02. Stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can home to the joint cavity and release various cytokines, thereby regulating the balance of T cells, ultimately achieving the goal of improving the anti-inflammatory activity of the environment and improving rheumatoid arthritis.
A clinical study using autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSC) in the treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis enrolled 9 patients and received BM-MSC infusion via intravenous injection. The results after treatment showed that the enrolled patients 'visual analogue scale (VAS) and DAS28-ESR (disease activity score 28-red blood cell sedimentation rate) were significantly reduced, regulatory T cells increased significantly, and Th17 percentage dropped significantly. The above results show that autologous BM-MSC can help improve the symptoms of refractory rheumatoid arthritis.
03. Stem cell therapy for multiple sclerosis
Studies have shown that after receiving umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) treatment, the bladder and intestinal symptoms have significantly improved;EDSS scores, sexual dysfunction and quality of life have also improved. In addition, MRI examinations of the head and cervical spine showed that the enrolled patients had no active lesions and no serious adverse reactions occurred during or after the intervention.
04. Cell therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease. The emergence of cell therapies such as stem cells and CAR-T cells has brought a turning point for this refractory disease.
A study on "stem cell therapy for SLE" enrolled a total of 18 patients. After receiving umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSC) treatment, the results showed that the patients had reduced proteinuria, improved renal function, and increased serum albumin. What is even more surprising is that other indicators of SLE, such as dsDNA (anti-double stranded DNA antibodies), ANA (antibodies and antinuclear antibodies) titers, SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI), serum complement C3, C4 concentrations, etc. There have also been improvements. Moreover, my country has also promulgated the "Expert Consensus on Stem Cell Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematous", further standardizing the treatment of the disease. Read the original text for details: Systemic lupus erythematosus can be saved| Thousands of patients have successfully used stem cells to fight wolves.
In addition to stem cells, another cell therapy, CAR-T cell therapy, is also making great strides in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
05. Stem cell therapy for inflammatory bowel disease
Several studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can restore the integrity of the epithelial barrier and be used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. In a "Phase 3 Clinical Study of MSC in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease", a total of 212 patients were enrolled and received adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSC) treatment. The results showed that after 24 weeks of treatment, comprehensive responses were achieved in both intent-to-treat (ITT) and modified ITT populations. In short, stem cell therapy is an effective, feasible and safe treatment method. It can significantly increase the fistula closure rate, improve CDEIS and CDAI scores, and help improve patients 'quality of life.
06. Stem cell therapy for autoimmune liver disease
Studies showed that 10 patients with primary biliary cholangitis After receiving allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSC) treatment, after 12 months of follow-up, the results showed that liver biomarkers of the enrolled patients (Including AST, ALT, GGT, IgM, and direct bilirubin levels), significantly reduced from baseline; Treg cell levels and IL-10 levels in peripheral blood monocytes increased, CD8 +T cell levels decreased, and the patient's quality of life improved, and no treatment-related side effects were found.
07. Stem cell therapy for Sjogren's syndrome
A clinical study on "stem cell treatment of Sjogren's syndrome" included a total of 24 patients with Sjogren's syndrome. After being enrolled and treated with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSC), the results showed that the patients had Sjogren's syndrome disease activity index (SSDAI), saliva flow rate increased, and the symptoms of Sjogren's syndrome were significantly reduced.
Message:
Stem cells have anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory properties, regenerative potential and multi-directional differentiation capabilities, and have shown great application potential in the treatment of various autoimmune diseases. While alleviating symptoms and improving autoimmune diseases, it also helps reduce or eliminate immune rejection, providing new hope for patients with refractory autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and Sjogren's syndrome!