
With the continuous maturity and breakthrough progress of stem cell technology, it marks that the direction of future medical care is being redefined. Cell therapy brings new treatment options and changes the limitations of traditional medicine. By fundamentally treating diseases, stem cell technology not only helps extend life, but also provides patients with a higher quality of life.

Existing drugs all act on enzymes, hormones, and receptors on living cells to produce therapeutic effects. Cell degeneration and death (such as Almerhets disease, commonly known as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's tremor paralysis, diabetes) and trauma (such as burns, spinal cord injury) require replenishing the number of living cells to maintain the function of tissues and organs. The rapid development of stem cell research has given people new hope for treating diseases. As early as 1999, the American magazine Science ranked stem cell technology as the number one scientific and technological achievement and the future of medicine.
Using drugs as a means to intervene in diseases is one of the important goals of medical research. Historically, with synthetic aspirin and recombinant human insulin as milestones, people have successively opened the era of chemical drug therapy and biopharmaceutical therapy. In 2017, the launch of Kymriah, a chimeric antigen receptor T cell product, marked mankind's move towards a new era of cell therapy.
Cell therapy is a treatment method that uses autologous or allogeneic cells as carriers and foreign gene-expressed proteins as acting molecules to repair tissues and organs. Cells are the basic unit of human body structure and function. Compared with molecular drugs, they can deal with more complex diseases as a whole. Cell therapy is supported by cell engineering, antibody engineering, genetic engineering technology and synthetic biology, and has developed rapidly in recent years.
Stem cells are a type of primitive undifferentiated cells with multi-directional differentiation potential and self-renewal ability, and have the potential to regenerate various tissues and organs of the human body. Stem cell drug development is a cutting-edge research area in life sciences. Stem cells have carried out extensive clinical trials in the treatment of different major and difficult diseases, and have been approved for marketing as drugs on certain indications, and have broad industrialization prospects.
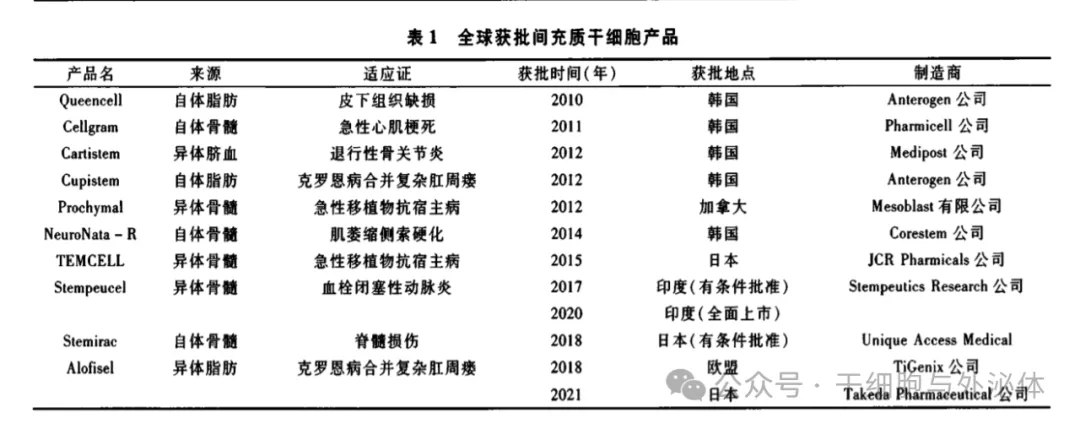
Stem cell therapy has always been one of the most valued cutting-edge areas in life sciences. In recent years, stem cell therapy research has developed rapidly, bringing hope to the repair and regeneration of tissues and organs and the solution of major refractory diseases. At present, there are a large number of new clinical research projects around the world every year, and the overall trend is on the rise.
Due to the huge potential of cell therapy, it is full of opportunities in future research in the field of medical and health. Stem cells have the potential to regenerate into various tissues, organs and human cells. Stem cell therapy achieves the purpose of treating diseases by transplanting healthy stem cells into patients to repair or replace damaged cells or tissues. Commonly used stem cells are divided into embryonic stem cells (ESC), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC).
On October 16, Guangming Daily/Guangming Net/Economic Reference and other media published or forwarded an article titled "Stem cells may trigger a medical revolution, a third treatment method after drugs and surgery." The main content of the article is as follows:
Regarding the development of stem cell therapy, the reporter interviewed relevant industry insiders. Regarding the two characteristics of stem cells, Gao Yansong, general manager of Jiuzhitang Meike (Beijing) Cell Technology Co., Ltd., gave an example that one is to pluck off the hair and blow it will turn into another monkey-it has the ability to self-replicate and regenerate, constantly self-renewing, dividing from one cell into two, two into four, and so on; The second type is the "seventy-two changes". Stem cells can change their form and differentiate from their original state into mature cells with specific functions under certain conditions.
In China, stem cell therapy products are in the stage of "quasi-dual-track system" supervision. Drug supervision requires companies to complete Phase 3 clinical trials and go on sale, while medical technology supervision requires the completion of clinical studies filed by the two committees and bureaus. At present, clinical research and transformation of stem cells are gradually focusing on drug management.
As of the end of 2023, a total of 140 research institutions across the country have passed the review and filing of stem cell clinical research institutions, and more than 110 stem cell clinical research projects have passed the review and filing. In addition, the National Center for Drug Evaluation has accepted more than 40 IND registrations for stem cell drugs, and 30 have entered clinical trials. Stem cell research provides an effective way to treat refractory diseases, and better clinical efficacy is worth looking forward to.
Re-program life
Why are stem cells so fascinating to the scientific community? The reporter interviewed Jia Yi, chief medical officer of Zehui Biotech, and said that stem cells have three abilities that can be used in disease treatment: "One is the immune regulation function, which reduces inflammatory cells and inflammatory damage by secreting various factors that inhibit inflammation. The second is to promote the damage repair function and repair local tissues by secreting factors to achieve a therapeutic effect. The third is to replace functions, replacing cells with reduced function or necrosis."
Take a piece of skin or a drop of blood, extract the cells, introduce specific transcription factors,"reprogram", transform them into pluripotent stem cells, and then further cultivate and differentiate. They will become various human cells, such as cardiomyocytes, retina cells, nerve cells, etc., and will eventually be expected to cultivate human organs without defects-this is not a fantasy, but a scenery that scientists may see as they follow the road opened by Nobuya Yamanaka.
If the above introduction is too complicated, you can also think of an organ as a big tree. Induced pluripotent stem cells are like a seed. After "watering" and "fertilizing", the stem cells can differentiate into different types of cells in the organ. Type, just like developing into leaves, trunks, and branches of a tree.
It is particularly worth mentioning that, as a type of pluripotent stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells have unique differentiation potential and functions, and are one of the earliest stem cell types in clinical application and are currently making the fastest progress. "Mesenchymal stem cells are like auxiliary players in a game. They play the role of anti-inflammation, immunoregulation and promoting tissue repair, and indirectly promote the regeneration of damaged tissues. In contrast, induced pluripotent stem cells are like the main players in the game. By differentiating into specific functional cells, they directly replenish cells in damaged tissues." Gao Yansong said.
The Spring of Regenerative Medicine
Currently, more than 6000 stem cell clinical trials under development around the world involve hundreds of diseases, including spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other difficult diseases. Countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom took the lead in using stem cell transplants to treat diseases and achieved certain curative effects. In my country, many hospitals have also carried out clinical research on mesenchymal stem cells to treat diseases.
"The safety of stem cell therapy is a top consideration. For example, in stem cell treatment of cancer, there are certain risks, which may lead to tumorigenesis, tumorigenesis, and tumorigenesis. This requires strict risk assessment to ensure its safety." Gao Yansong said that clinical trials need to be conducted in consideration of the safety of stem cell drugs, appropriate indications must be selected, and clinical trial plans should be designed for corresponding symptoms. Subsequently, the test was conducted in accordance with the current clinical trial specifications to obtain reliable and real data, and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for marketing in accordance with the drug standards.
In terms of effectiveness, Jia Yi mentioned that the research and development of stem cell drugs should not only focus on meeting the corresponding symptoms and symptoms of aging, but also take into account the research and development layout of stem cells to accurately position and improve efficacy. For example, based on pluripotent stem cells, they can differentiate into functional cells., as a functional drug, it corresponds to different diseases.
In addition, in the research and development of stem cell drugs, it is necessary to increase the production scale of stem cell drugs and control costs while ensuring quality. "At present, the international mainstream production method is still manual production, with limited output, high cost, and less benefits to patients. In the next step, industrial breakthroughs need to be made to further enhance the production capacity of stem cell drugs." Gao Yansong said.
The industry believes that with the continuous development of technology, stem cells will surely trigger a medical revolution and become the third treatment method after drugs and surgery. Awakening the "Monkey King" in our bodies, maybe it can really have different abilities.